The Journey of the Megalethoscope
| Written by | Alicia Halligan |
|---|---|
| Published | 6/1/2020 |
The Journey of the Megalethoscope
| Written by | Alicia Halligan |
|---|---|
| Published | 6/1/2020 |
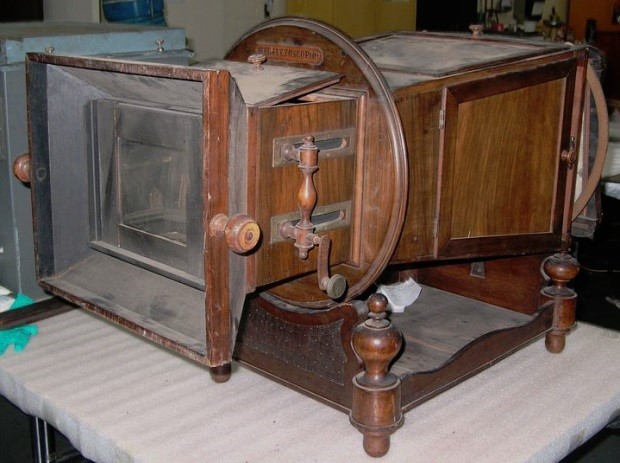

The Megalethoscope during treatment in the lab.
The Megalethoscope is one of thousands of objects from The Henry Ford’s Collections Storage Building (CSB) that is being conserved, digitized, and rehoused thanks to a ‘Museums for America Collections Stewardship’ grant from the Institute of Museums and Library Services (IMLS), received in October 2017. Heading behind the scenes, this blog will explain the process that an artifact moves through from conservation to photography—and eventually, becoming viewable on Digital Collections.
Conservation Treatment
Once an artifact is selected, tagged, and inventoried, it is given a preliminary cleaning with a vacuum and transported into the Conservation Lab.
(Left) Photo of how the Megalethoscope was found in storage; (Center) The instruction panel that shows how the Megalethoscope works; (Right) The Megalethoscope mounted correctly on its stand.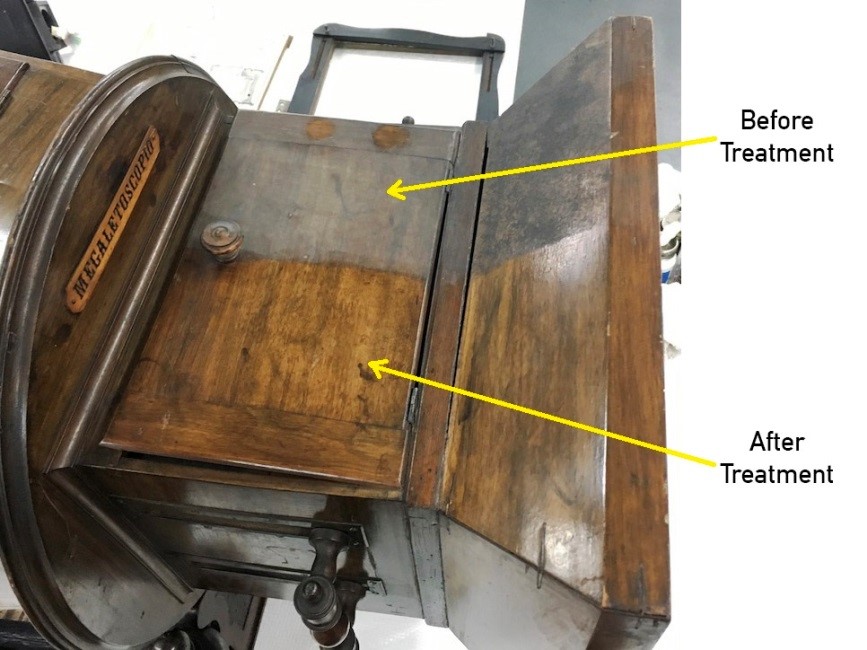
The top panels on the Megalethoscope before and after it was cleaned and waxed.
Prior to cleaning, a small spot was tested to determine the best method and materials to use. A mild detergent, diluted in distilled water did the best cleaning job without damaging the wood. The cleaning solution was gently rubbed on the wood surfaces with swabs to remove all of the dirt and grime, and then the surface was cleared with distilled water to remove soap residue. To bring back the shine of the wood finish, furniture wax was applied and buffed.
Years of storage on its end had caused the joints of the Megalethoscope’s viewer to separate (highlighted in red). Damaged areas were repaired removing the old, dried-up glue, and replacing it with fresh glue.
Large shrinkage cracks had developed in the two side panels that serve as light reflectors, and in the back panel that covers a large pane of glass. Shrinkage cracks develop when wood expands and contracts because temperature and humidity levels fluctuate too much.
Since the cracks were big enough to see through (approximately 1/8th inch wide) thin strips of Japanese tissue paper were soaked with a reversible adhesive, then dried, to fill each of the cracks. As each strip of tissue was compacted into the cracks, the adhesive was activated with solvent. This caused the dry paper to adhere to the edges of the crack and create a bridge. This fill was smoothed down flush with the rest of the wood panel, providing an even surface that could be in-painted to match the adjoining wood panels.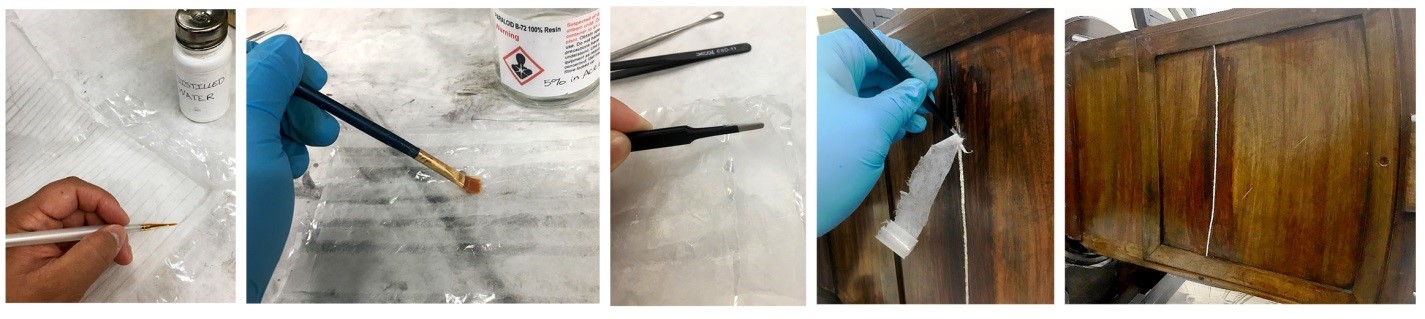
Using Japanese tissue to fill shrinkage cracks.
Watercolor and acrylic paints were used on the paper fills to hide the repairs and to paint in the large scratches and abrasions that covered the body of the Megalethoscope. To give the painted areas the same shine as the wood finish, a topcoat of acrylic gloss medium was applied.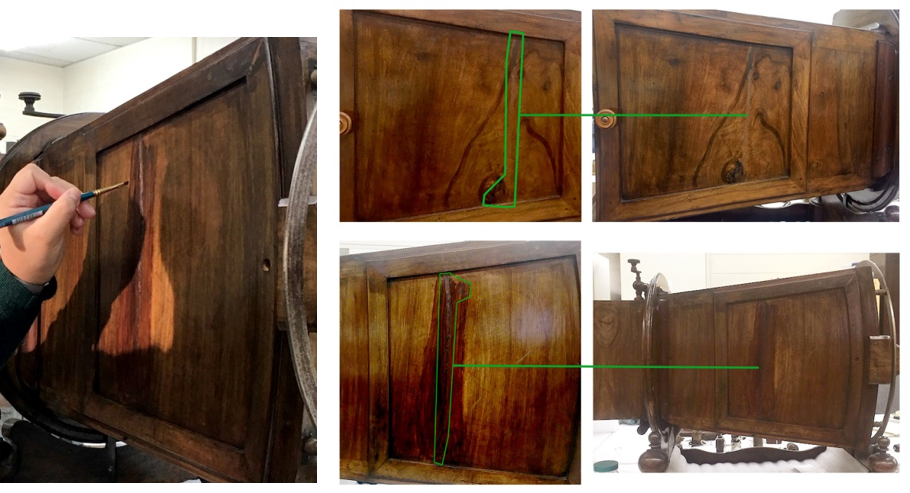
(Left) In-painting the paper filled cracks; (Right) Paper fills after they were painted (in green).
To finish the treatment, the glass and mirror pieces of the Megalethoscope were cleaned with a solution of ethanol and distilled water, then wiped with microfiber cloths to prevent streaking. Any metal parts were cleaned with a mild solvent to remove small areas of corrosion and then waxed and buffed them to bring back their shine.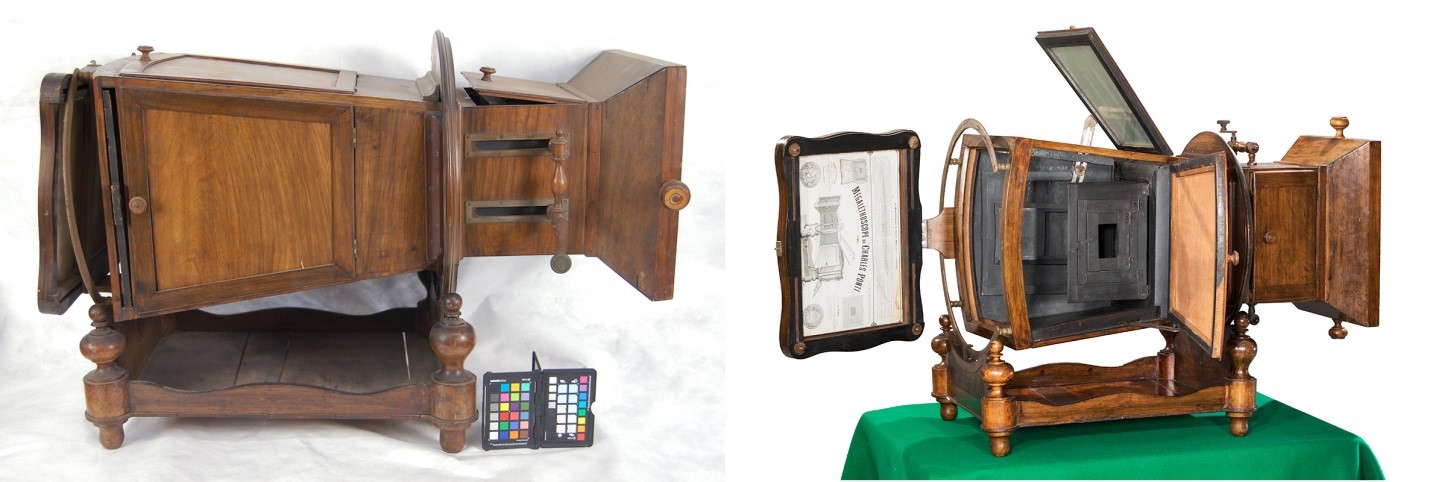
The Megalethoscope (Left) before and (Right) after conservation treatment.
Investigating Megalethoscope Slides
During treatment, an original photographic slide left inside of the Megalethoscope was discovered. This led to additional investigation. The slide depicted is of the Ponte dei Sospiri in Venice (the Bridge of Sighs). We wondered if there were more of these slides in the collection and after checking our collections database, found a box labeled “Megalethoscope Slides” in the Benson Ford Research Center (BFRC). The contents of the box were not catalogued, so we decided we needed to go to the Archives to see for ourselves!
When the box was brought to the Reading Room at the BFRC, we opened the box and found 21 slides, all in good condition! Many of the slides were photographs of Italy and Paris, plus a handful depicting interiors.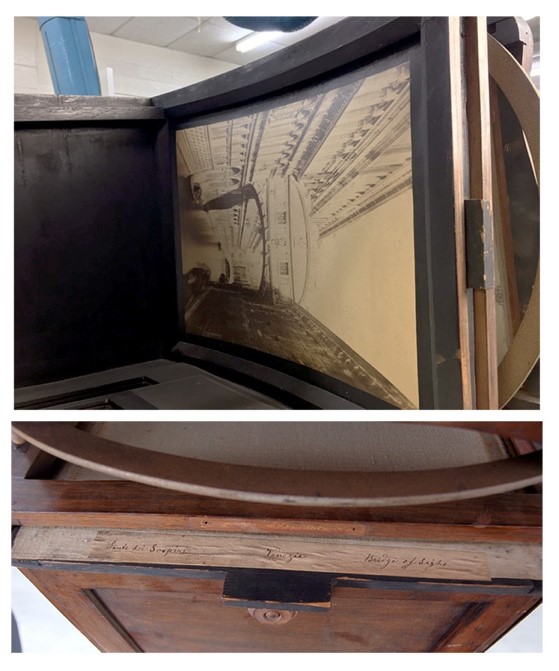
(Top) The Ponte dei Sospiri slide with handwritten inscription (Bottom) inside the Megalethoscope after it was taken out of storage.
Megalethoscope slides are large, multi-layered assemblies. Each slide consists of an albumen photographic image with pin pricks matching the areas where there is a light source or reflection (ex. an illuminated cityscape). Behind it are layers of colored tissue or cellophane and sometimes extra imagery when lit from behind; finally, there is a backing of a thinner, translucent canvas. All of this is stretched over a curved wooden frame. The curve creates a stereo view of the image which encompasses the viewer’s sight lines when they place their head into the Megalethoscope, much the way today’s virtual reality goggles work. Light is directed onto the slide to create different effects.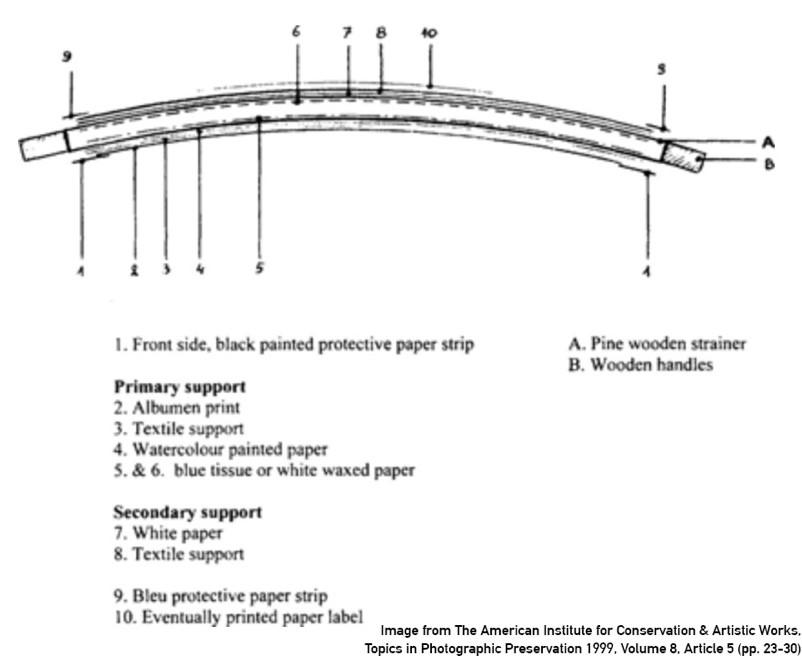
Cross section of a Megalethoscope slide. (Image courtesy of The American Institute for Conservation & Artistic Works, Photographic Materials Group Journal, Topics in Photographic Preservation 1999, Vol. 8, Art.5 (pp.23-30).
The slide that was found with the Megalethoscope in storage did not have any color effects, so we were excited to find that the majority of the slides in our archives had variations in color and optical illusions. The slides were moved to the conservation lab, where their surfaces were gently vacuumed. A smoke sponge removed any remaining dust and dirt. A few of the slides had small punctures or tears to the canvas, but since they were stable, we decided to not repair them at the present. We were thrilled to be able to reunite the slides with the Megalethoscope and have a fully functioning artifact!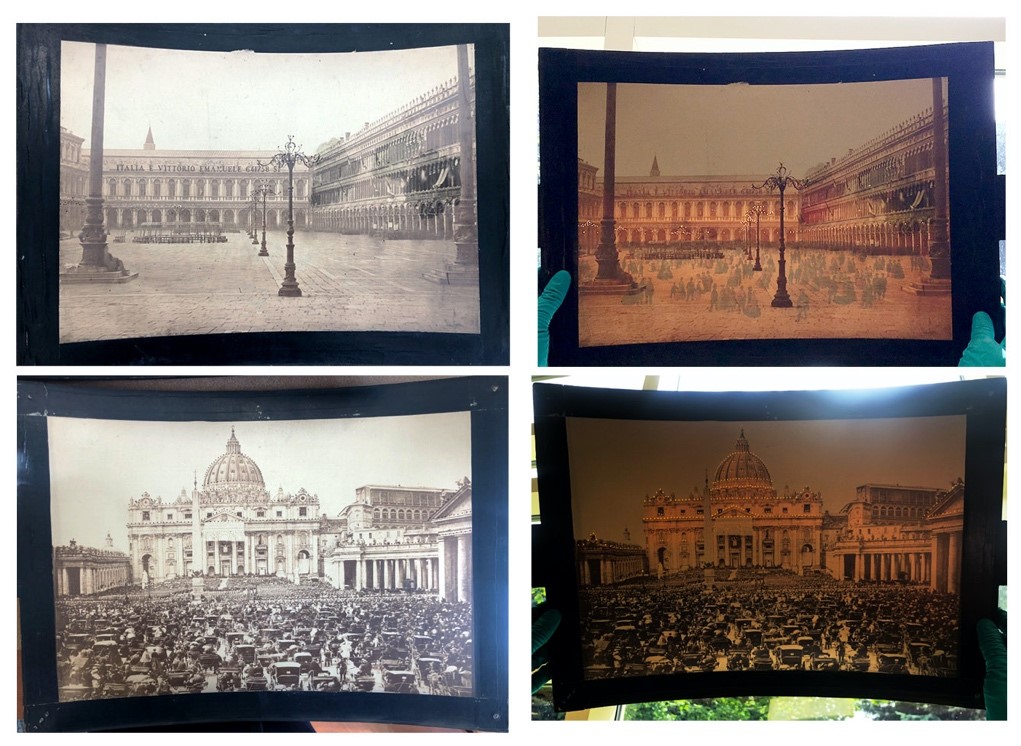
(Top Left & Right) In "St. Mark's Square” you can see how people appear when light is applied to the image.
Photographing the Megalethoscope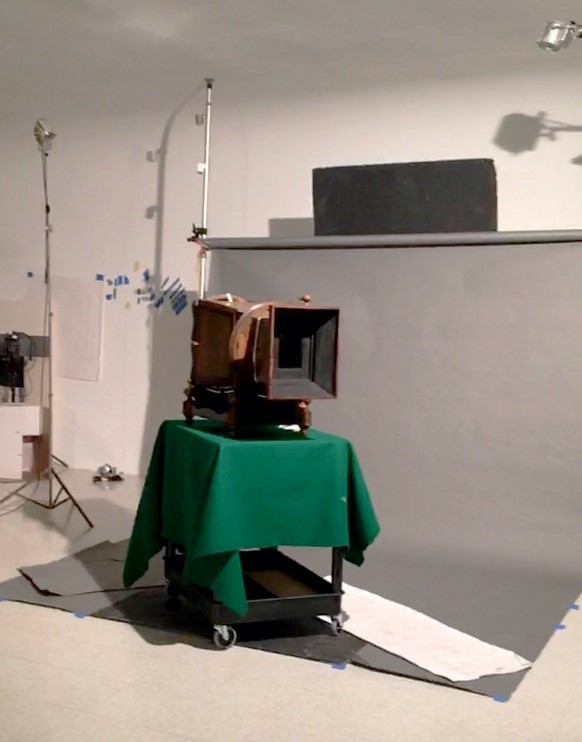
The Megalethoscope on a cart for ease of movement during photography.
There are many steps that artifacts go through to be digitized and made available online, especially for objects as complex as the Megalethoscope. After the slides were conserved and cataloged, they were brought to the photography studio. For 3-D artifacts like the Megalethoscope, photography typically includes an image of the front, the back, and each side, if necessary. Photos serve as a reference material for historical researchers, and they document the condition of the artifact at that time.
The slides needed to be photographed in two ways: as they appeared in normal light, and as they would be seen through the Megalethoscope. Our senior photographer Rudy Ruzicska came up with a very clever arrangement to recreate this effect by placing two sets of milk crates with a sheet of Plexiglas suspended between them. He placed lights directly under and at an acute angle above the Plexiglas. The slides were placed in the middle of the Plexiglas with black paper border around the edges to prevent any light glare.
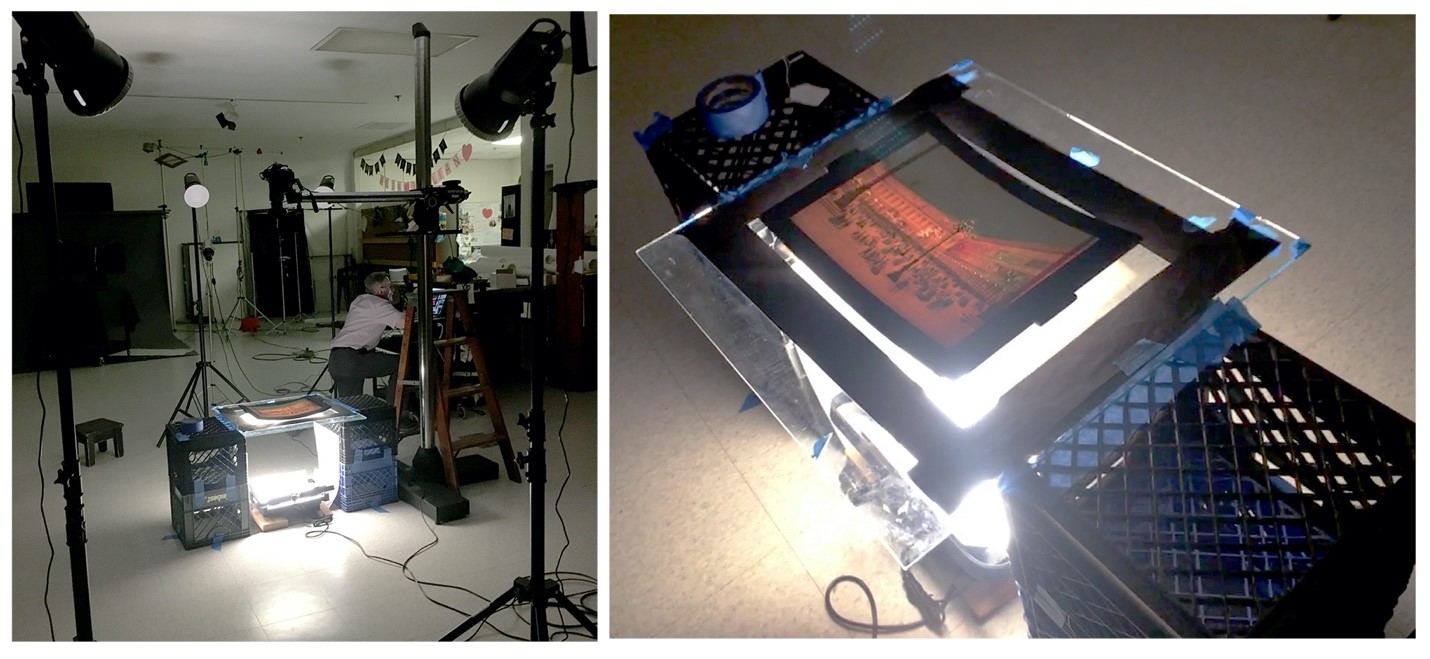
Light arrangement for photography of Megalethoscope slides. (Left) Rudy shooting with his custom set-up during the dark shot of the “St. Mark’s Square” slide; (Right) A closer view of the set-up.
The Megalethoscope images were then photographed under normal (“daytime”) light to document their appearance, and with their “nighttime” illumination effect by turning off the studio lights. The first time we saw the images illuminated in the dark, we all gasped – they became so vibrant and magical!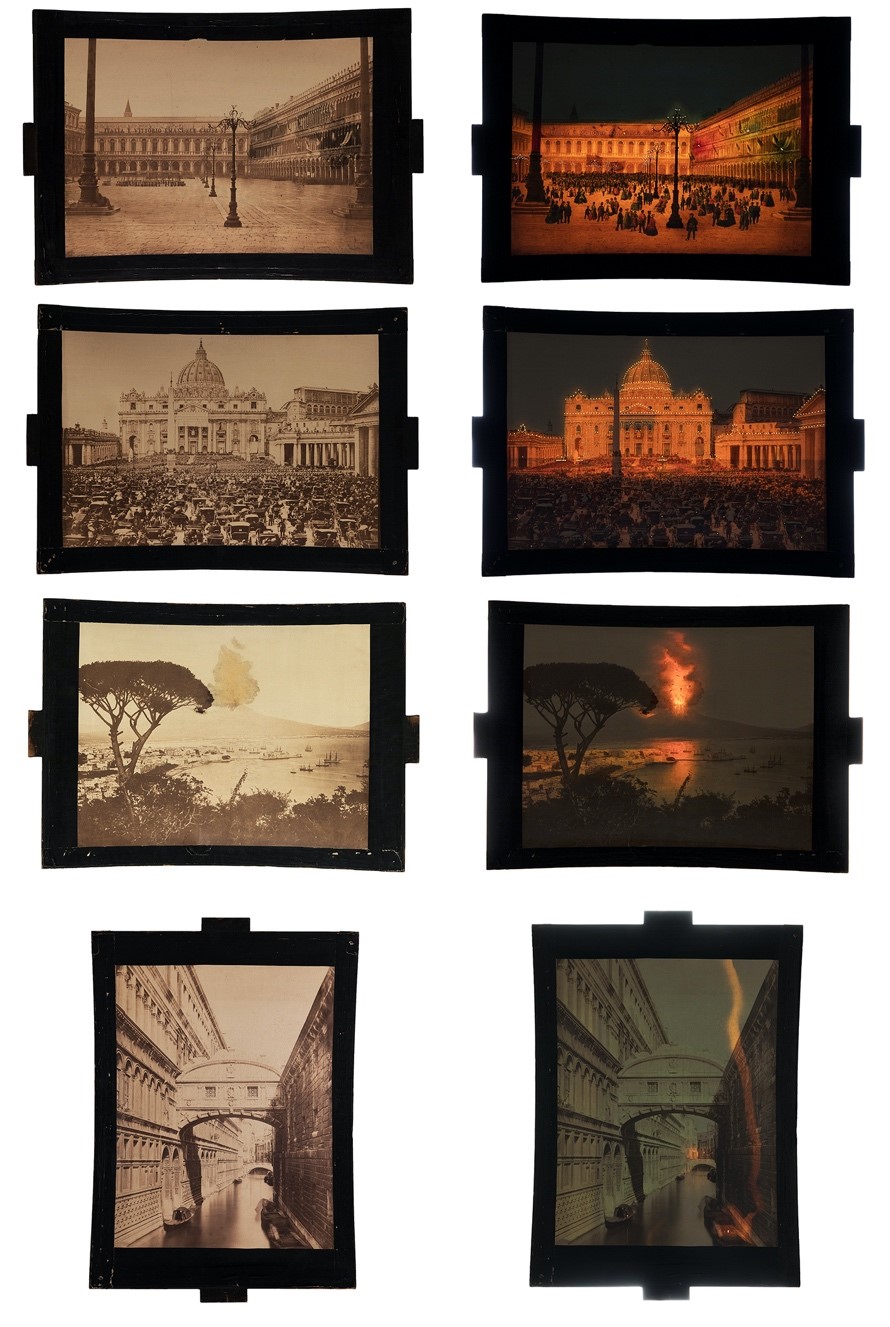 
A selection of the final images, with color and effects as they would have been seen inside the Megalethoscope.
The Megalethoscope was re-housed in a specially designed box which will store the unit and its base together safely, along with all of the slides. It was then moved to permanent storage in the Main Storage Building (MSB), as have most of the artifacts that we have worked on during the IMLS grant.
Thank you for joining me on this behind-the-scenes journey of an artifact from storage, to conservation, and through to digitization. I hope you enjoyed the ride!
Alicia Halligan is an IMLS Conservation Specialist at The Henry Ford
Keywords | |
|---|---|
Themes |
