"The Busy World" Automaton
| Written by | Jeanine Head Miller |
|---|---|
| Published | 1/10/2022 |
"The Busy World" Automaton
| Written by | Jeanine Head Miller |
|---|---|
| Published | 1/10/2022 |
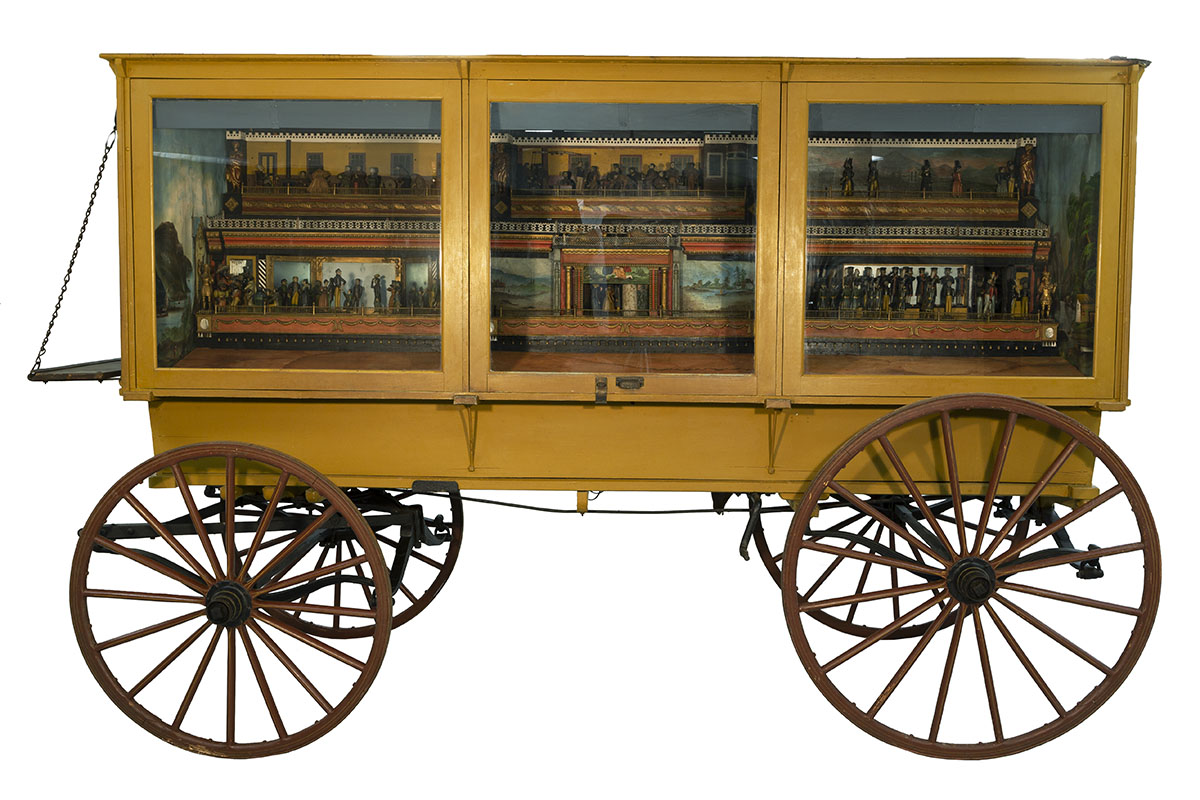 “The Busy World” automaton, 1830–1850. / THF187282
“The Busy World” automaton, 1830–1850. / THF187282
I was about nine years old when I first saw it. My family and I were visiting Henry Ford Museum when I spotted “The Busy World”—an intriguingly detailed and well-populated automaton displayed along the museum’s Street of Shops displays. I was entranced. “The Busy World” would remain among my most vivid memories of this visit. Little did I know that many years later I would be involved in further research on this fascinating, whimsical object.
An automaton is a non-electric moving machine that performs a predetermined set of operations. With approximately 300 moving figures, “The Busy World” automaton is a kind of mechanized diorama with six individual platforms powered by gears, belts, and pulleys. When the automaton is cranked, the figures go into motion.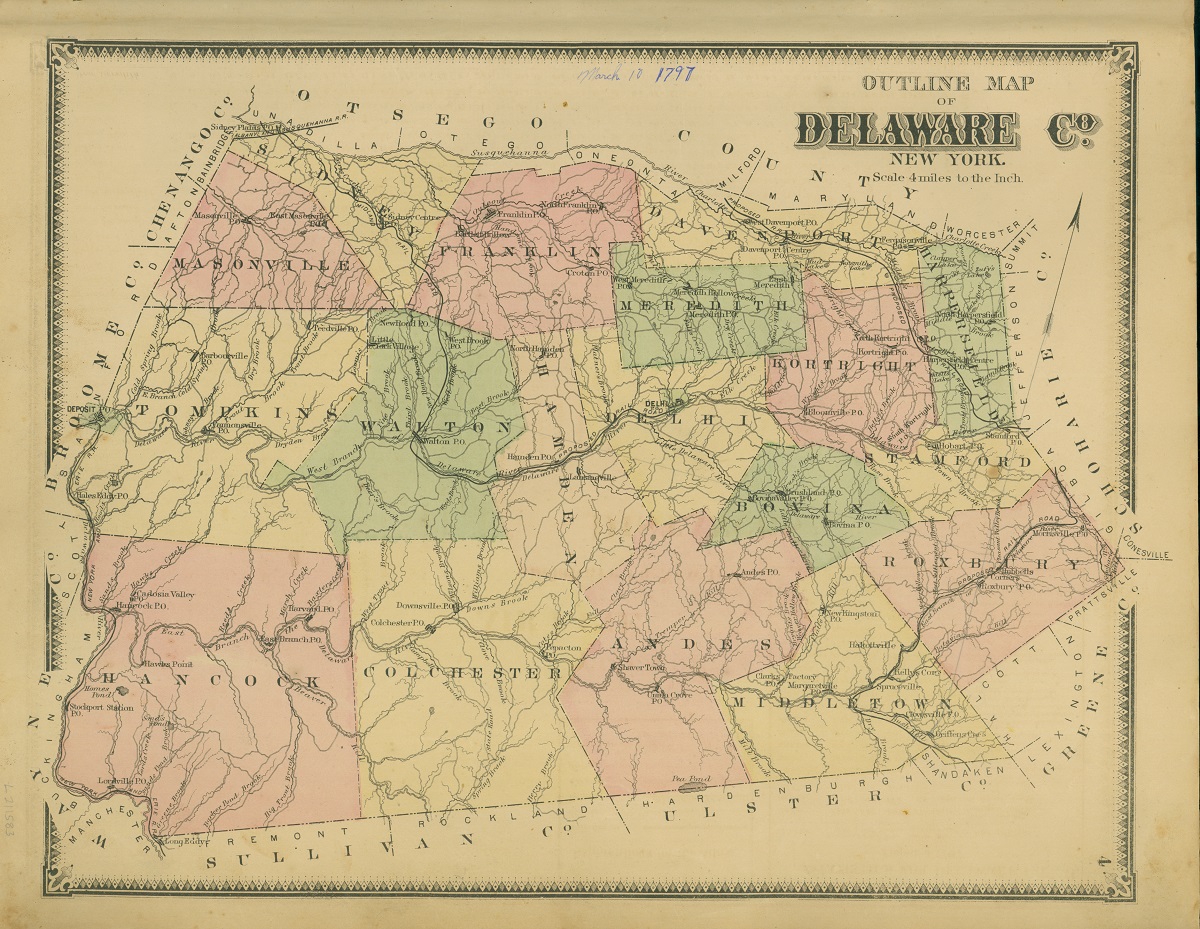
1869 Beers Atlas map of Delaware County, New York. / Image courtesy of the Delaware County Historical Association
Delaware County in upstate New York—where “The Busy World” was likely built and spent much of its working life—was a place of farms and small villages during the 19th century. The wagon's lively, hand-cranked animations would have had tremendous popular appeal for adults and children alike at country fairs and small exhibitions.
“The Busy World” features six different animated scenes. Click on the links under the scenes below to see those images in our Digital Collections, where you can zoom in on the details.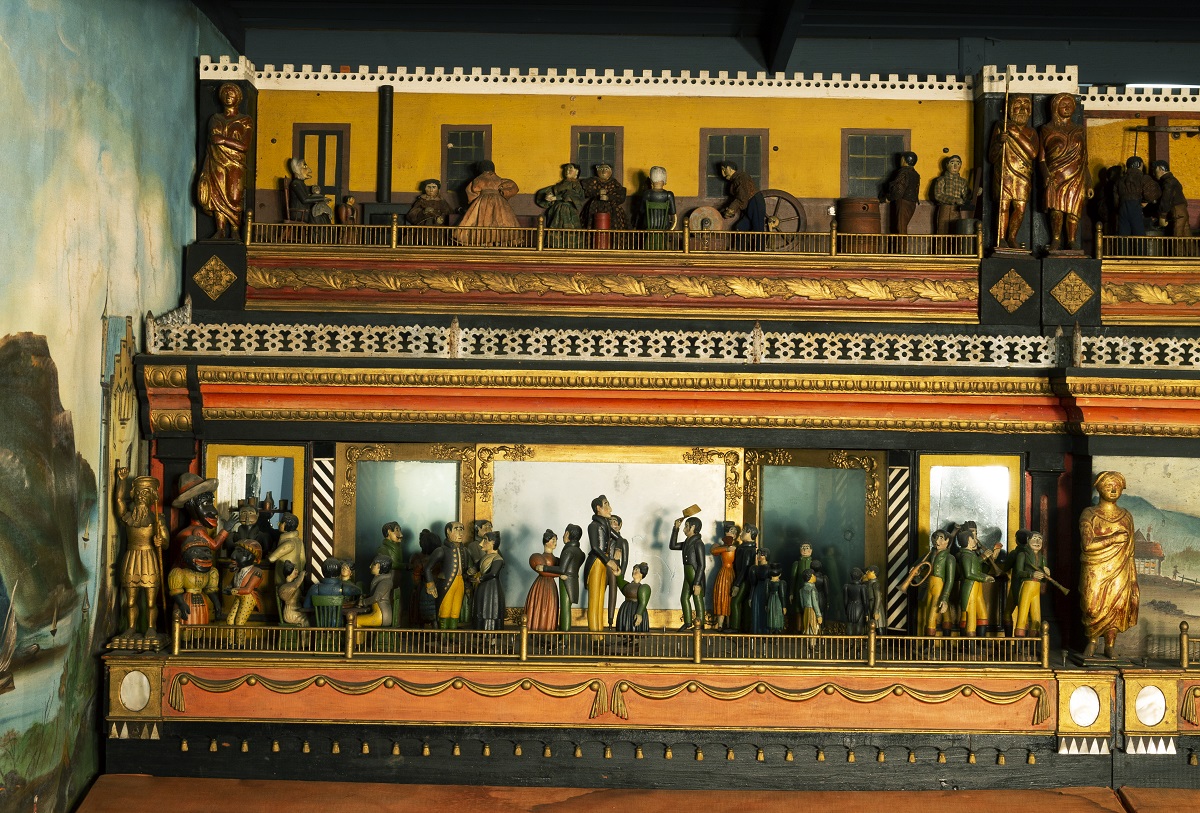
Left section of “The Busy World.” / THF187276, detail
At the upper left, figures perform activities of everyday life, including rocking a baby, getting warm by the stove, chopping food, spinning thread, churning butter, and sharpening a tool.
In the scene at lower left, people attend a ballroom dance while musicians play. At the left of the dance scene are caricatured figures of African Americans. This “Busy World” scene reflects not only the activities of the time period but also the racism of the era.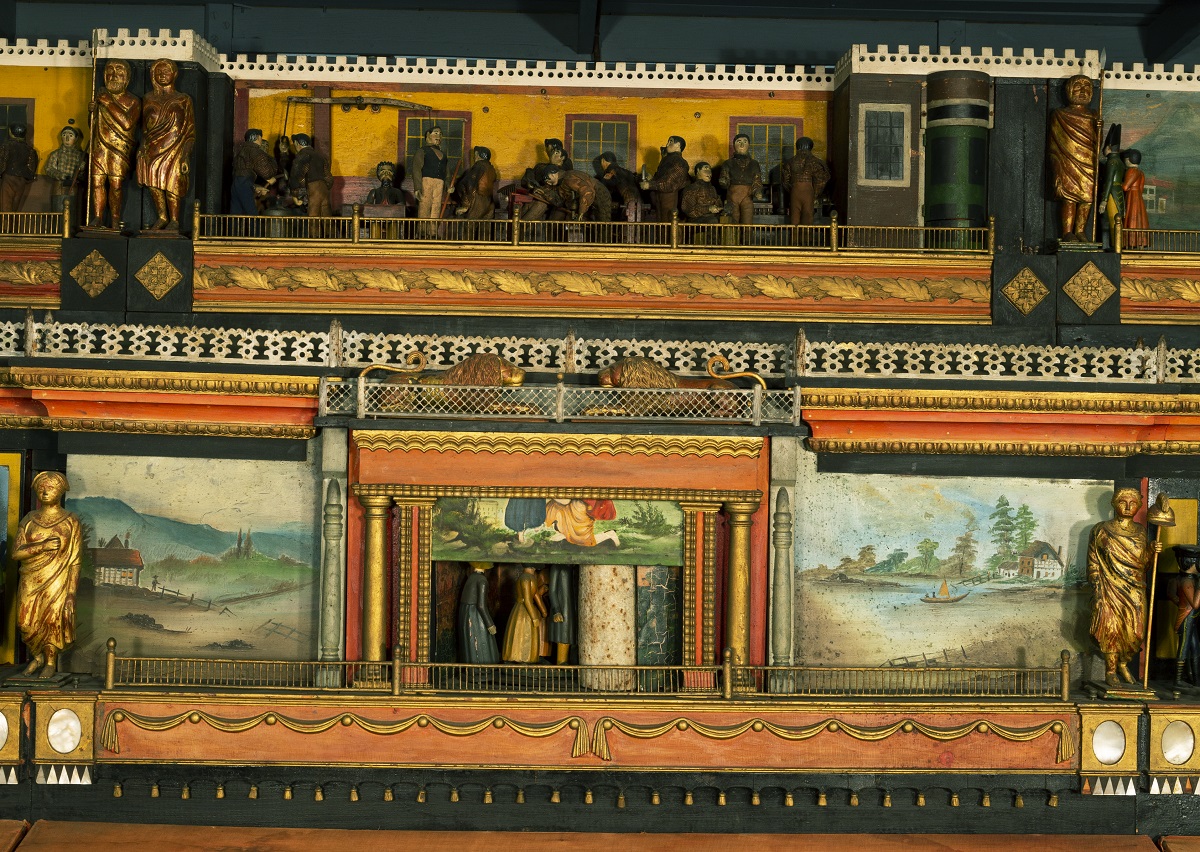
Center section of “The Busy World.” / THF187277, detail
The scene at upper center shows men making rakes and grain cradles in a factory. Delaware County had at least one rake factory. During the early 19th century, New York was the grain belt of the United States. Wooden rakes were essential tools on farms.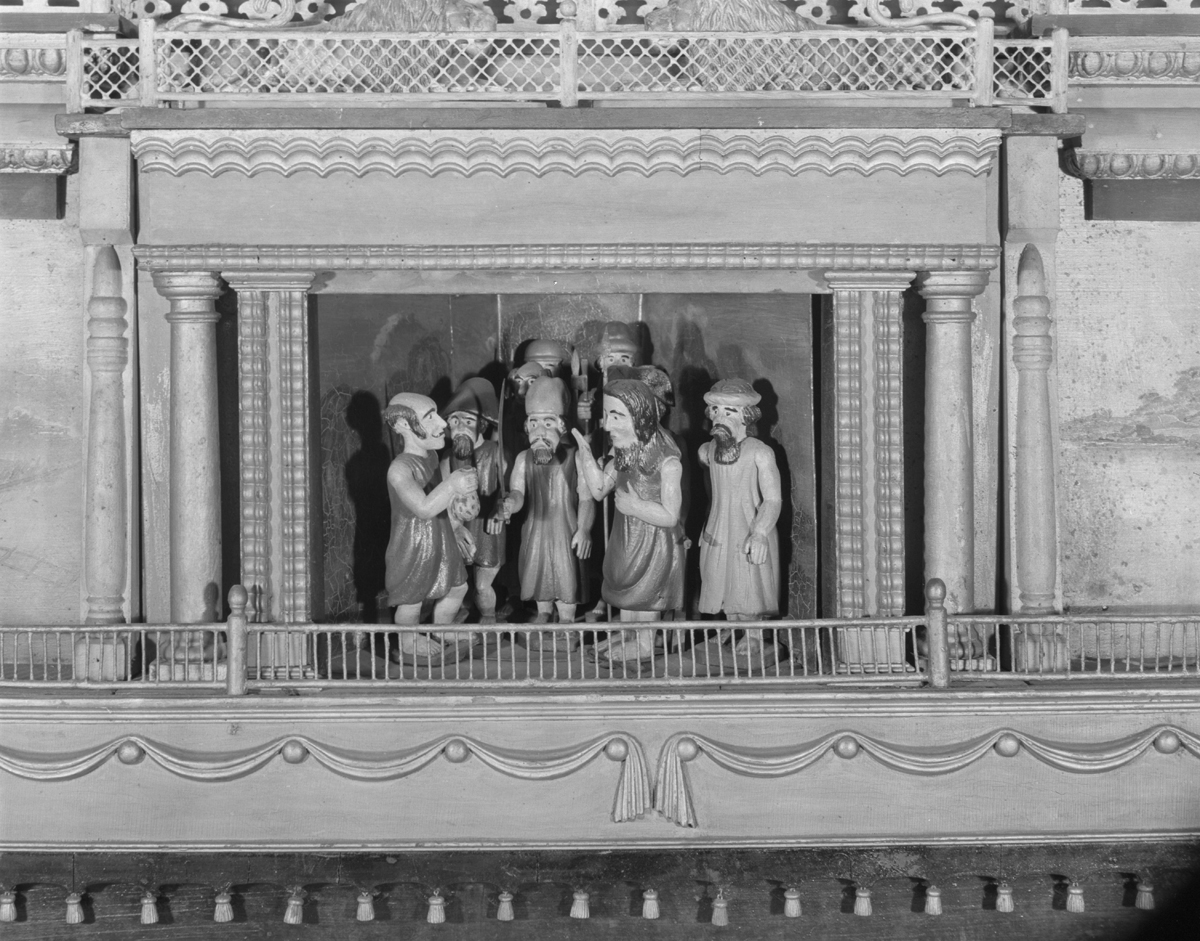
Biblical scene from “The Busy World.” / THF125152
At lower center, a small revolving “stage” features eight Biblical stories.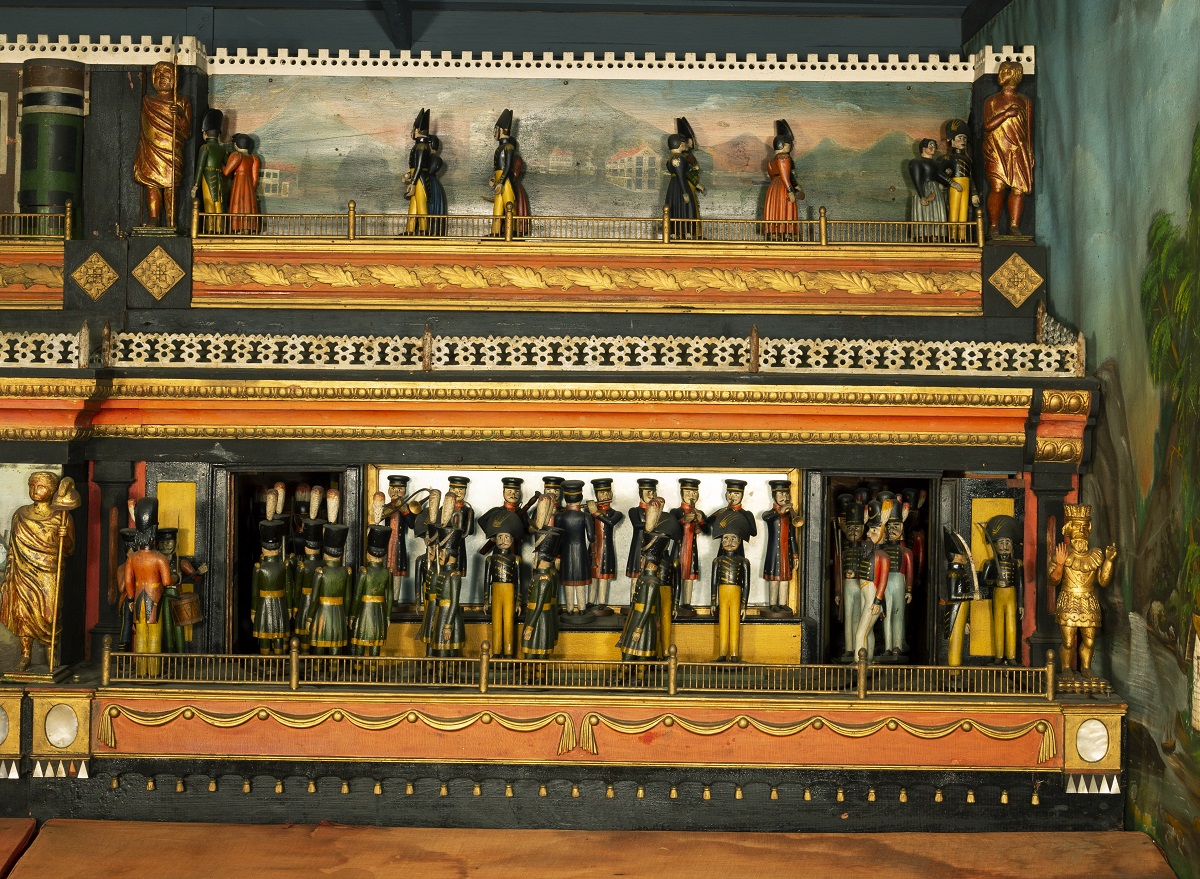
Right section of “The Busy World.” / THF187278, detail
At upper right, soldiers in uniform promenade with ladies.
The scene at lower right features a regiment of soldiers parading in formation to the “sounds” of a military band.
“The Busy World” Comes to The Henry Ford
“The Busy World” came to The Henry Ford in 1963. The museum purchased the automaton from Janos and Mary Williams of Stone Henge Antiques in Sidney, New York. Where was it before that? Well, we know part of the story.
The Williamses had acquired “The Busy World” from a man named David Smith. About 1944, David Smith (1923–2002) saw an ad in a Walton, New York, newspaper offering “The Busy World” for sale: “Will sell cheap, if sold this week, ONE busy world.” Twenty-one-year-old Smith, who lived in nearby Delhi, New York, couldn’t resist. He drove the 17 miles to Walton to take a look. Amazed and delighted with what he saw, Smith purchased the automaton with his own savings, over the objections of his family. For the first seven years that he owned it, Smith stored “The Busy World” in his family’s barn in Delhi. David Smith got it to run, at least sporadically.
It wasn’t until September 1951 that “The Busy World” once again had a public showing. David Smith’s mother had offered the family barn to the Delaware County Horticultural Society as a place to hold their annual Harvest Show. “The Busy World” delighted local people who came to see the choice vegetables, flower arrangements, and potted plants on display there. Some of those attending recalled 30 or so years before when the automaton had appeared at county fairs in the area.
Next stop for “The Busy World”? David Smith opened an antique store in his hometown of Delhi, where he displayed the automaton. The name of the shop? Busy World Antiques.
David Hoy Takes “The Busy World” on the Road
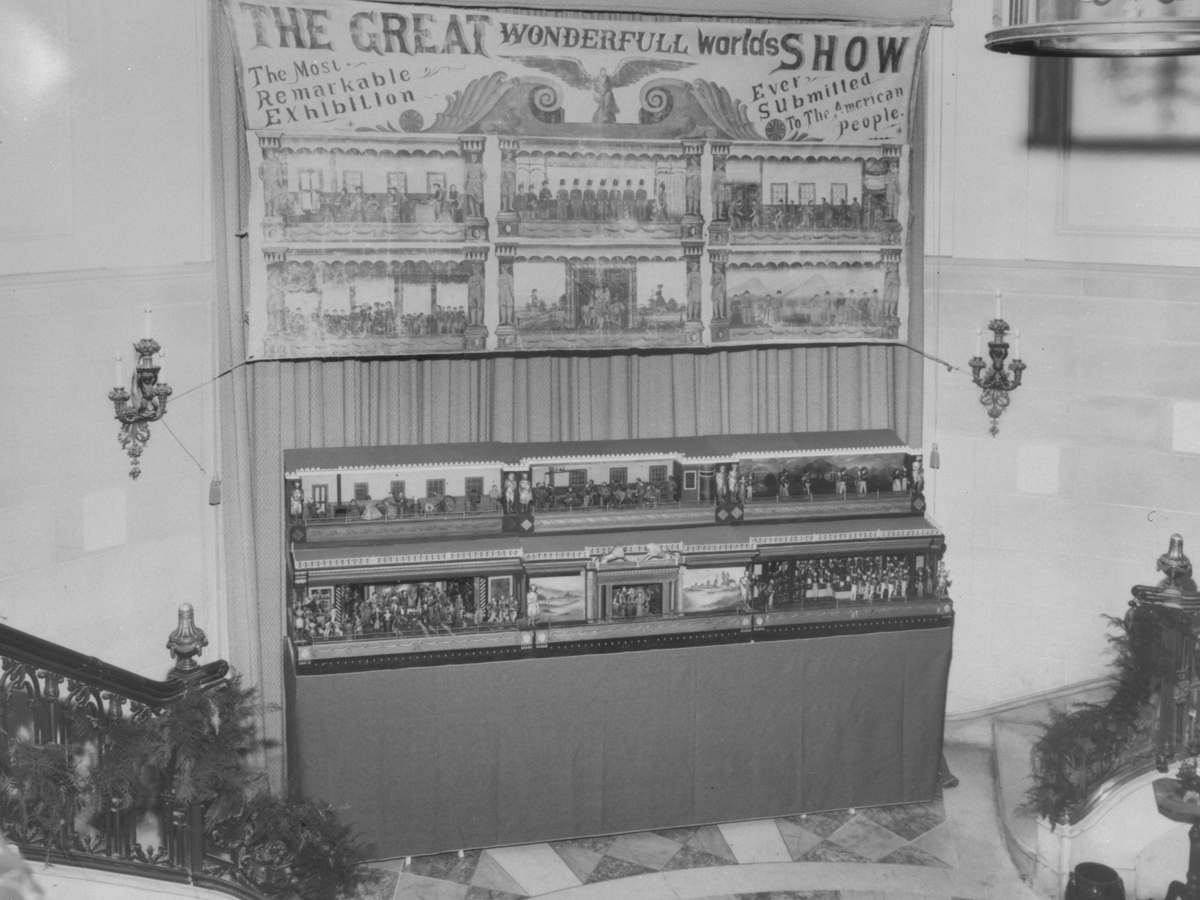

“The Busy World” platforms exhibited in an unidentified location, probably in the early 20th century. An advertising banner hangs above—one that may date from the late 1860s or 1870s. / THF125153
David Smith had purchased “The Busy World” from Elizabeth Hoy Thomas (1874–1949). She was the daughter of David Hoy (1848–1934), the man who exhibited “The Busy World” at local fairs and carnivals at the turn of the 20th century. According to David Smith, Elizabeth Hoy Thomas told him that “The Busy World” took 17 years to build and was constructed by two men—one carved the figures and the other assembled the machinery.
David Hoy’s 1934 obituary recalled Hoy’s yearly exhibitions of the “World at Work” or “Busy World” automaton at local fairs. Hoy is said to have charged five or ten cents to see “The Busy World” in motion. David Hoy exhibited “The Busy World” regularly until the mid-1910s, and then for one last time at the Walton Armory in late 1933. After his death the following year, the automaton remained in a shed at Hoy’s daughter’s home in Walton. She placed the newspaper ad offering it for sale about ten years later—the ad seen by young David Smith.
These tickets were found in the wagon. They appear to date between 1890 and 1910 and may have been used as “The Busy World” made the rounds of country fairs and carnivals in the latter portion of its career. In Latin, androides means “resembling a man,” and was used during the 19th century to describe an automaton resembling a human being in form and movement. / THF187284
Looking for Answers
We had many unanswered questions about “The Busy World.”
Curatorial research volunteer Gil Gallagher worked many months to dig up some answers, trolling census records and countless newspapers online. Ray LaFever, archivist at the Delaware County Historical Association, lent his research skills and familiarity with Delaware County history to the quest. Here’s what their research turned up.
When they sold it, antique dealers Janos and Mary Williams mistakenly told The Henry Ford that “The Busy World” had been built by David Hoy. And that he “began it in 1830 and took 17 years to make it.” As we found, not quite so—at least the part about David Hoy. Our research showed that Hoy didn’t build it. He acquired the automaton sometime later.
The general dates given for the construction of “The Busy World” appear to be correct. The figures and objects shown in the scenes reflect the era of the 1830s—including the women’s fashions, the Franklin heating stove (upper left section), and the serpent, a musical instrument (lower right section).
Therefore, David Hoy couldn’t have made it. Hoy was born in Bovina in Delaware County—but not until 1848. His family moved to Iowa when he was ten. By the mid-1870s, Hoy returned to Delaware County, where he married and had three children. During the following decades, he would make his living as a farmer, carpenter, stone mason, and teamster. Hoy must have acquired “The Busy World” sometime after he returned to Delaware County as an adult. (A 1905 newspaper article noted that the automaton was “now run by a Walton man, David Hoy,” so someone else probably toured it before Hoy.) The wagon that now carries “The Busy World” was a later addition—one likely added by Hoy, who mounted the automaton figures and machinery in the wagon to make it easier to transport. (One newspaper article mentions that the automaton platforms were originally displayed in a tent.)
So, we found some answers—yet questions remain.
Was the automaton originally called “The Busy World”? It seems that it may have acquired that title in the late-19th or early-20th century, since it is not mentioned on the banner or tickets.
And, despite all our efforts, the identities of the original makers of “The Busy World”—whoever these talented individuals were—remain a mystery for now.
Jeanine Head Miller is Curator of Domestic Life at The Henry Ford. Many thanks to Sophia Kloc, Office Administrator for Historical Resources at The Henry Ford, for editorial preparation assistance with this post.
Keywords | |
|---|---|
Themes |
