Winter Railroading Was No Holiday
| Written by | Matt Anderson |
|---|---|
| Published | 12/8/2021 |
Winter on the railroad was a miserable season, and there were no holidays for railroaders, essential workers of the mid-19th century.
Winter Railroading Was No Holiday
| Written by | Matt Anderson |
|---|---|
| Published | 12/8/2021 |
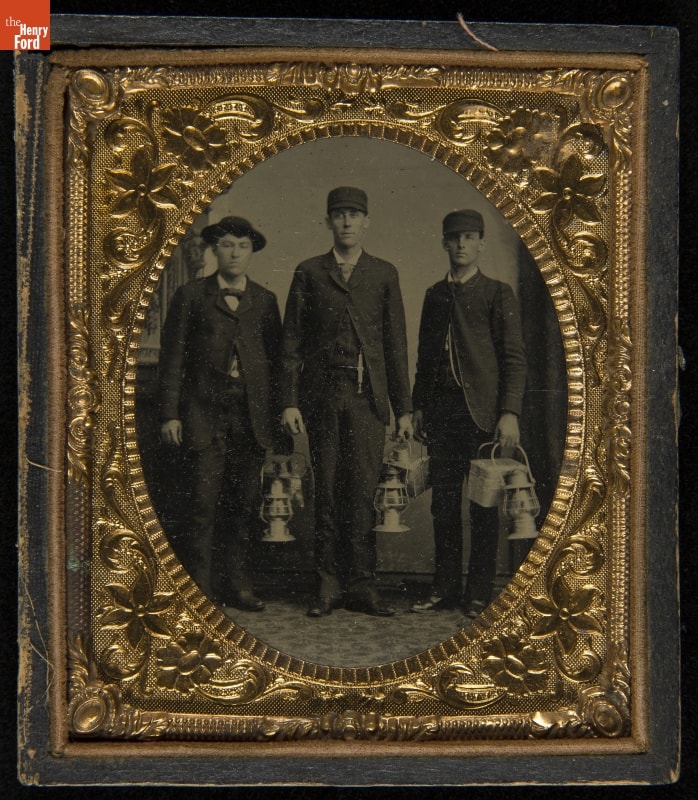 For many 19th-century railroaders, holidays were workdays like any other. / THF286590
For many 19th-century railroaders, holidays were workdays like any other. / THF286590As we gather with family and friends to celebrate the holidays this year, many of us will enjoy a day (or several days) away from the job. But for our essential workers, time off may not be an option. For those who do the daily work that makes modern life possible, a holiday is just another day. In the mid-19th century, the railroader was America’s preeminent essential worker. (Don’t get me wrong—railroaders are still essential workers in the early 21st century, but their industry isn’t as prominent in today’s culture.) Trains had to roll, tracks had to be kept clear, and freight had to move—no matter what the calendar said.
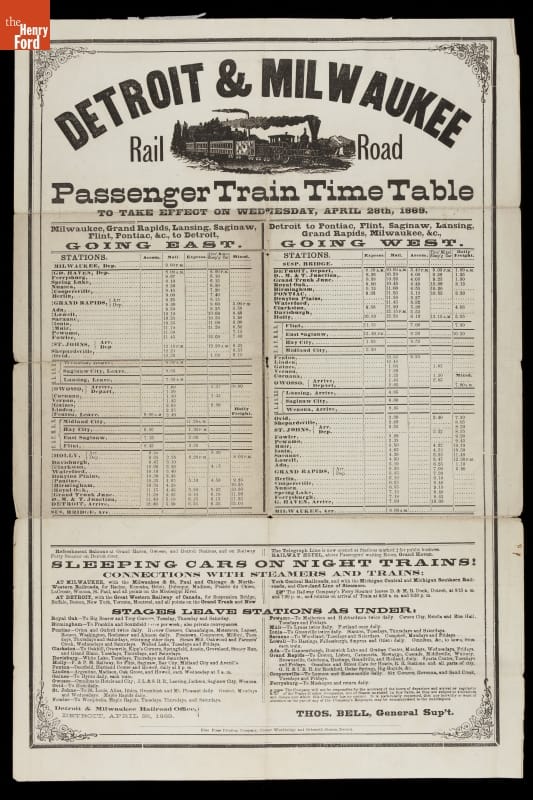
The railroad’s timetable was gospel, holiday or not. / THF203346
Mainline railroading was a 24/7 operation. It was possible to shutter most operations at a roundhouse for a day, and railroads could cancel the local trains that served nearby industries, but longer-distance through freight and passenger trains had to keep moving. Stop a train somewhere and you block that track—and all the other trains that need to use it. Before long, the whole system grinds to a halt. (Today’s passenger airlines experience the same problem when bad weather shuts down a hub airport. Delays cascade throughout the entire network. But airlines can “reset” each night when far fewer flights operate. That’s an advantage railroads have never enjoyed.)
Conductors, engineers, fireman, brakemen, and others often spent their holidays either out on the line or bunking in a railroad dormitory far from home, waiting for their next run. And there might be miserable weather to contend with too. In northern states, December meant cold and snow. Consider the plight of a mid-19th-century brakeman. In the days before George Westinghouse’s air brake, the only way to stop a train was to manually set the individual handbrakes on each car. When the engineer gave the signal, brakemen had to scramble along the roofs of the railcars and spin the iron wheels that applied those brakes. It was a dangerous job in fair weather, but it could be deadly when ice and snow made everything slippery. On a windy night, a brakeman might be blown off into a snowbank below—where he hoped his crewmates noticed his absence before the train went too far.
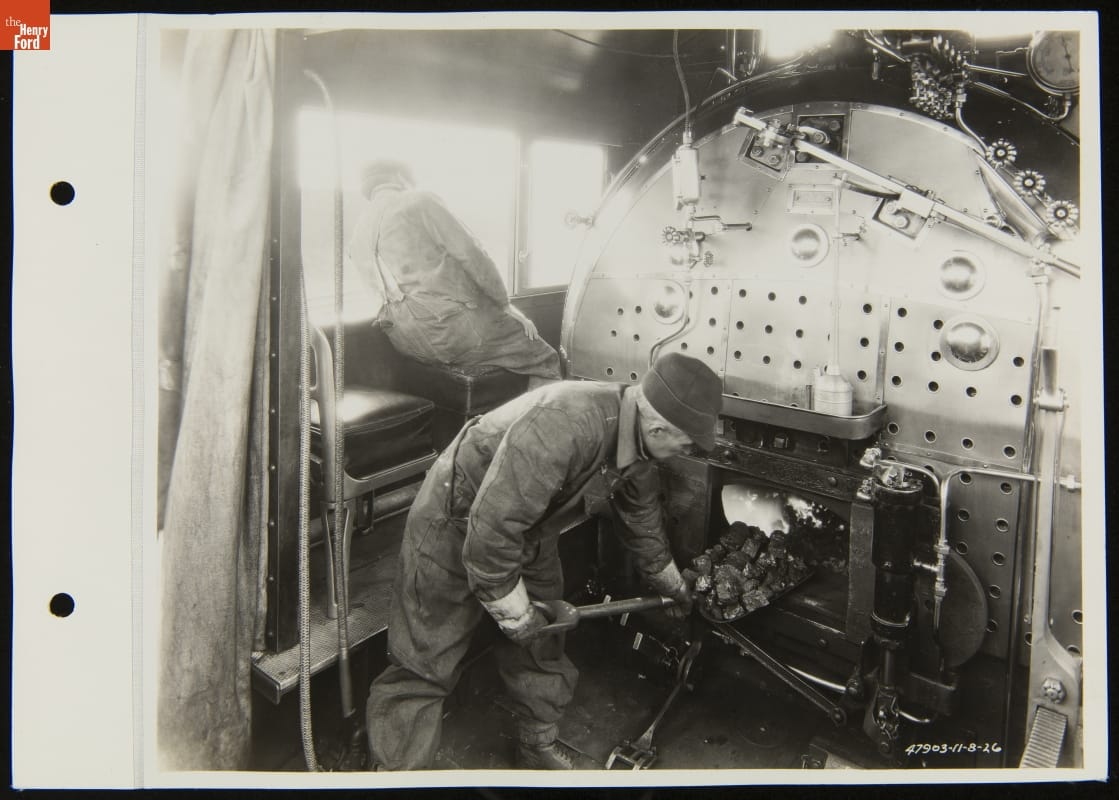

The firebox kept a locomotive’s cab warm throughout the year—a decided advantage in winter. / THF286564
For the engineer and fireman in the locomotive cab, life was somewhat better. They stayed warm even through the coldest winter days due to the heat from the locomotive’s firebox. (There were surely more than a few enginemen who preferred the cold to sweltering summer days, when cab temperatures were hellish.) But there were still challenges. Snow and ice on the rails required extra skill to keep the locomotive’s wheels from spinning when climbing a long grade. Falling snow obscured the track ahead, making it difficult to see signal lights and lanterns—or an unexpected stopped train.
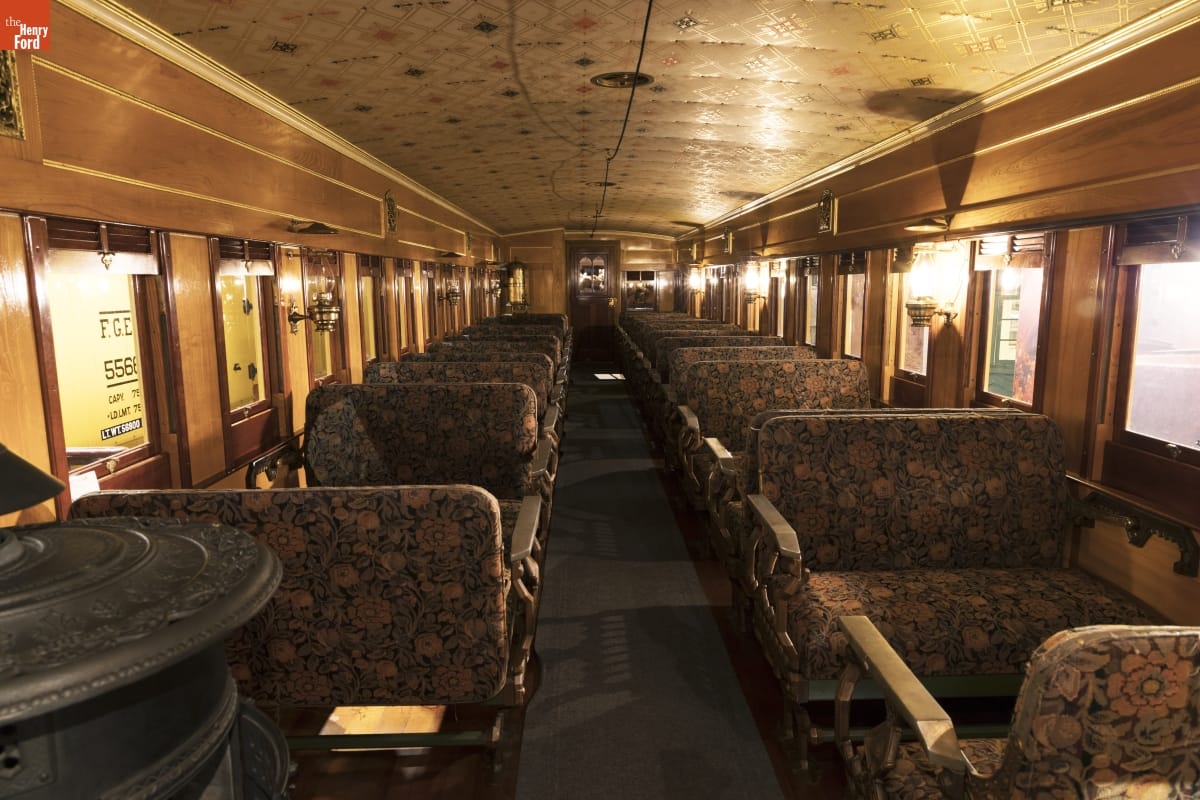

Polished passenger cars were aesthetically pleasing. They were also highly combustible, should the coal stove (at lower left) tip over in an accident. / THF176785
Riders on passenger trains also stayed out of the weather, but even they had their struggles. Wooden passenger cars were drafty. In the mid-19th century, heat came from a single coal stove in each car. Inevitably, those seated far from the stove shivered, while those seated nearest to it sweated. Given that cars of this period were heavily varnished and trimmed with any number of flammable fabrics and surfaces, coal stoves also posed a serious fire hazard.
Two of America’s worst railroad disasters involved December fires. On December 18, 1867, an eastbound express train derailed while crossing a bridge near Angola, New York. The last car plummeted off the bridge and its stove came apart, scattering hot coals over the wreckage. Forty-nine people are believed to have died in the wreck—most of them burned in the resulting inferno. Newspapers referred to the carnage as the “Angola Horror.”
Nine years later, another bridge-fire accident occurred at Ashtabula, Ohio. On December 29, 1876, a faulty bridge collapsed under the Pacific Express as the train headed west. This time, 11 passenger cars fell into the chasm and an estimated 92 people lost their lives. Some were killed in the crash itself, but others succumbed to the fire ignited by spilled coals and fueled by wooden wreckage. The “Ashtabula Horror” exceeded that of Angola and would remain America’s deadliest railroad accident for more than 40 years.
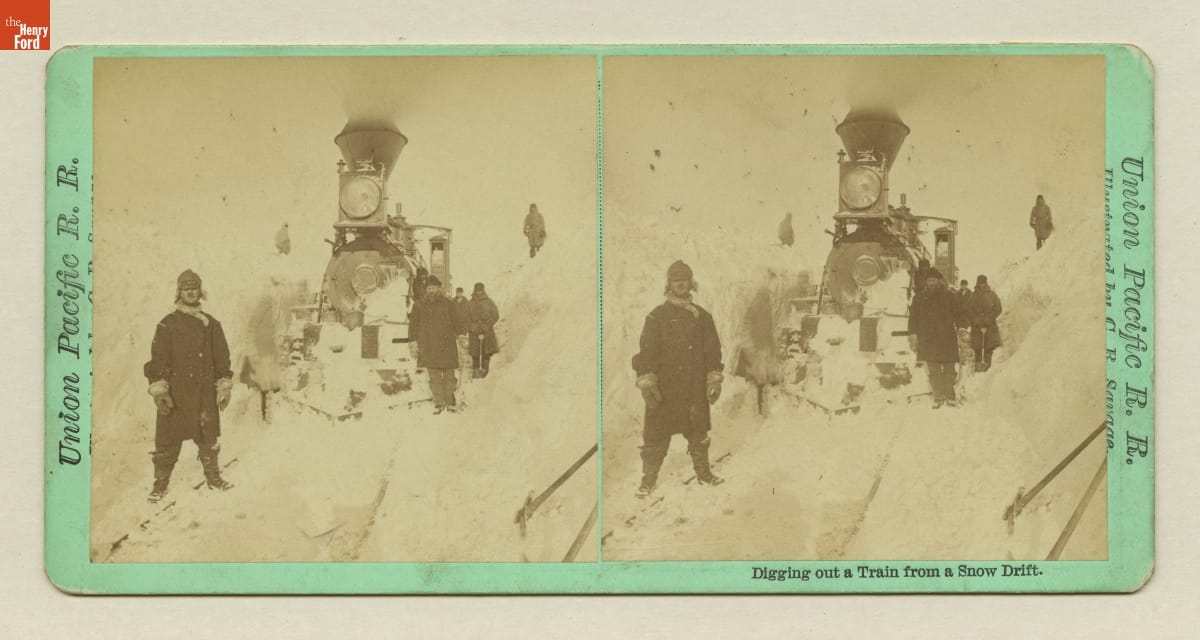

Clearing snow was the most backbreaking task on the railroad in winter. / THF120726
Trains didn’t go anywhere if the track was blocked, so in snowstorms track crews battled fiercely against falling and drifting snow to keep the way clear. Brute force and backbreaking effort were their best tools. Large plows, pushed by powerful locomotives, threw snow clear of the right-of-way. When the crew encountered a particularly deep or stubborn blockage, there was little choice but to back the plow up for some distance, then open the throttle and hit the drift hard and fast. With luck, the plow pushed through and continued on its way, or at least made a sizeable dent before another try. The worst-case scenario had the plow stuck so deep into a drift that it couldn’t be extracted. When that happened, crew members simply had to shovel it, however long it took. Powerful rotary plows—essentially, snowblowers for railroad track—made the job easier when they arrived in the 1880s, but these expensive machines were generally only used on mountain railroads in the American West.
By any measure, winter on the railroad was a miserable season.

Artist (and automotive designer) Virgil Exner captured a more romantic vision of winter railroading in this painting from about 1970. / THF36304
Later in the 20th century, as working conditions and passenger safety improved, and as steel coaches and steam heat replaced wooden cars with coal stoves, the railroad found a happier place in our holiday culture. Trains became synonymous with trips back home to visit loved ones, and electric train sets became staples under the Christmas tree—whether as gifts or as decorations. More recently, popular movies like The Polar Express have continued the trend. It may be that there were no holidays on the railroad, but it’s equally true that our holidays wouldn’t be what they are today without it.
Matt Anderson is Curator of Transportation at The Henry Ford.
Additional Readings:
Keywords | |
|---|---|
Themes |
