Posts Tagged african american history
Deepening Our Understanding of Soybeans
 Soybean Processing for Fiber and Oil, Ford Exposition, New York World's Fair, 1939 / THF216213
Soybean Processing for Fiber and Oil, Ford Exposition, New York World's Fair, 1939 / THF216213
A New Partnership
Today, on National Agriculture Day, The Henry Ford is pleased to announce a new partnership with the Michigan Soybean Committee to deepen our understanding of this important crop, from field to factory.
The Michigan Soybean Committee works on behalf of Michigan’s 12,000 soybean farmers to drive demand, fund research advancements, share the story of agriculture, and identify ways to help farmers grow soybeans sustainably for generations to come. Michigan Soybean Committee has a renewed focus on consumer outreach and working with partners to provide information to the public about soybeans and agriculture in the state of Michigan. The collections of The Henry Ford help tell the long history of soy, and especially the launch of the legume in Michigan, a project with a long history dating back to Henry Ford himself. Michigan Soybean Committee is excited to work with The Henry Ford to provide the public with the chance to learn more about agriculture and the innovations that have helped farmers feed the world.
Soybeans Planted in 30-inch Rows / Photo courtesy Michigan Soybean Committee
Why Soybeans?
The soybean (soya bean, Glycine max) moved from relatively obscure forage crop in 1920 to center stage on global markets in 2020. Today soybean farmers in 19 states, including Michigan, raise 96% of the more than 4 billion bushels of beans produced in the United States. Each of those soybeans contains oil, protein, and biomass, attributes that processors use to transform the soybean into valuable products.
Mrs. Hardy Checking Soybean Milk in Ford Lab, March 1944 / THF272478
Today we encounter soybeans in almost every aspect of our daily lives, but we may not recognize the legume, even when we use or consume it. Drink soymilk? Use a non-dairy creamer or whipped topping? Eat chocolate? Use soy oil for cooking? Is your candle made of soy? How about the bioplastic coating your take-out food container or disposable coffee cup? Have you ever filled your vehicle with biodiesel? These products, and many more, likely include ingredients derived from soybeans. The Michigan Soybean Committee recommends the United Soybean Board website https://soynewuses.org/ as a good resource to learn even more about all of the products made with soy.
Presto Whip Building, Dearborn, Michigan, 1976 / THF115752
Why Soybean Stories from The Henry Ford?
Our founder, Henry Ford, was intrigued by and invested in research on the humble soybean, both as a food source and for use in industrial products. Our collections contain much information on these topics. You can read more about “Soybeans: Henry Ford’s Miracle Crop,” or explore related artifacts in this Expert Set that illustrates Henry Ford’s soybean research, some of which took place at the Soybean Laboratory (now the Soybean Lab Agricultural Gallery) in Greenfield Village. A clip from the first season of The Henry Ford's Innovation Nation features host Mo Rocca and Matt Anderson, Curator of Transportation at The Henry Ford, in the Soybean Lab discussing “Different Uses of Soybeans.” Content related to that episode includes a soyfoods Expert Set and one of our most popular research inquiries from guests, information about Henry Ford’s soybean plastic car.
Robert Boyer and Henry Ford in a Soybean Field, 1936 / THF98619
Black chemists contributed to this soybean research. Paul Foster focused on food research. “Paul Foster and Food Research in Henry Ford’s Laboratories, 1930-1942” introduces readers to Foster and explores some of the soy recipes that resulted from research he conducted. George Washington Carver and his assistant, Austin Curtis, Jr., chemists working at Tuskegee Institute in Alabama, shared Henry Ford’s enthusiasm for chemurgy (industrial uses for raw materials). Both Carver and Curtis participated in the third Dearborn Conference on Industry in 1937, featuring lectures by chemists working with farm-grown crops and industrial products, and Curtis even worked one summer in Ford’s Greenfield Village Soybean Lab. Ford expanded soy food research in 1942 with dedication of the Carver Nutrition Laboratory on Michigan Avenue in Dearborn, near Greenfield Village.
Ford Motor Company shared its soybean research at World’s Fairs during the 1930s. The Ford Exposition exhibited the William Ford Barn (now in Greenfield Village) transformed into “the industrial farm of the future” at the 1934 World’s Fair in Chicago. Giveaways included a souvenir box containing items from the Earth (including soybeans) used in Ford manufacturing. At the 1936 Texas Centennial Exposition, Ford Motor Company handed out salt-and-pepper shakers converted from gear shift knobs made from soy products. Ford staff demonstrated chemical experiments used to extract oil and transform it into fiber during the 1939–1940 New York World’s Fair.
Soybean Processing for Fiber and Oil, Ford Exposition, New York World's Fair, 1939 / THF216215
Coming Soon
What do we have in store for this partnership?
We’ll kick things off on March 23 on The Henry Ford’s Facebook page, with an interview with Laurie Isley, Michigan farmer and president of Michigan Soybean Committee. You can get a sneak peek of Isley’s work at the websites for U.S. Soy and the Michigan Agriculture Council.
John Deere Tractor and Planter Planting Soybeans / Photo courtesy United Soybean Board
Our plans for 2022 focus on exploring untold stories, adding to existing stories, and engaging the public in the process. We will explore changes in biological and mechanical technologies between 1920 and 2020, and document agricultural research at Ford farms focused on producing soybeans richer in oil content and better suited to industrial uses. We will deepen existing content on the daily operations of soybean research undertaken at the chemical laboratory constructed by Henry Ford in Greenfield Village in 1928 (still standing today), and in the George Washington Carver Nutrition Laboratory launched by Ford in 1942.
Over the growing season, we’ll explore the year-round work it takes to produce soybeans in Michigan, from planting to growing to harvesting, with the farmers who do this work. This will also involve a collaborative contemporary collecting effort to document Michigan soybean farmers today and add those stories to the permanent collections of The Henry Ford.
Case IH Combine Harvesting Soybeans / Photo courtesy Michigan Soybean Committee
The Michigan Soybean Committee will share its popular teacher resources with The Henry Ford’s learning and engagement staff. This will benefit rising fifth graders in The Henry Ford’s 2022 Growers summer camp, presented by the Michigan Soybean Committee, as they explore soya from bean to bioplastic. From June to August, students in the Growers summer camp will interact directly with Michigan Soybean Committee resources and soybeans growing in Greenfield Village for the first time since the 1940s.
Cultivating and Planting Activity at Soybean Laboratory, Greenfield Village, Dearborn, Michigan, 1937–1950 / THF236443
Both The Henry Ford and Michigan Soybean Committee are eager for this 2022 soybean-knowledge growing season, and we look forward to having you along for the journey.
Debra A. Reid is Curator of Agriculture and the Environment at The Henry Ford. Many thanks to the Michigan Soybean Committee for their collaboration on this post.
Ford Motor Company, world's fairs, African American history, Henry Ford, Greenfield Village, Greenfield Village buildings, food, research, soybeans, philanthropy, agriculture, by Debra A. Reid
 Austin W. Curtis (left) assisting George Washington Carver (right) during a lecture at Starr Commonwealth for Boys School, Albion, Michigan, 1939. / THF213740
Austin W. Curtis (left) assisting George Washington Carver (right) during a lecture at Starr Commonwealth for Boys School, Albion, Michigan, 1939. / THF213740
Austin Wingate Curtis, Jr. (1911–2004) assisted George Washington Carver for nearly eight years (1935–1943). Biographers often measure Curtis by his association with Carver, the renowned Black scientist who spent his career at Tuskegee Institute (now Tuskegee University). Mark D. Hersey described Curtis as “Carver’s best-known assistant” in his 2011 biography of Carver, titled My Work Is That of Conservation (page 181).
Curtis might be Carver’s best-known assistant, but his association with Carver accounted for only eight of Curtis’s ninety-three years. After Carver’s death, Curtis remained at Tuskegee until 1944 when the board decided not to retain him. He relocated to Detroit, Michigan, launched a business that emphasized his association with Carver, raised a family, pursued various business ventures, ran for political office, and added to The Henry Ford’s collection documenting George W. Carver. The following provides a fuller picture of Austin Curtis.
The Early Years
Austin Wingate Curtis, Jr., was born July 28, 1911, in Kanawha County, West Virginia. Support for education ran deep in his family. His maternal great-grandfather, Samuel I. Cabell (1802–1865), owned the land that the state acquired to build the West Virginia Colored Institute (which became the West Virginia Collegiate Institute in the early 20th century and is now West Virginia State University). This was one of 17 Black land-grant institutions that the Morrill Land-Grant Act of 1890 partially funded by 1920.
Austin Curtis’s mother, Dora Throne Brown (1875–1960), enrolled at West Virginia Colored Institute to train as a teacher. His father, Austin Wingate Curtis, Sr. (1872–1950), graduated in 1899 from the Black land-grant college in North Carolina (now North Carolina A&T State University at Greensboro). He began teaching agriculture at the West Virginia Institute that same year. He and Dora Brown married in 1905. They had two children, Alice Cabell Curtis (1908–2000) and Austin Wingate Curtis, Jr.
The Henry Ford has no photographs of the Curtis family, but the Library of Congress does. These provide a rare glimpse into rural Black culture during the period when more Black families owned land than at any other time in U.S. history (approximately 25 percent of Black farmers nationwide identified as landowners in the 1920 census).
A support system operated out of the Black land-grant colleges that linked farm families to information shared by experts trained in agriculture and domestic science. Tuskegee Institute’s moveable school drew a lot of attention from the media, and might be the best-known example of the ways that experts reached farmers across the countryside, but it was one approach among many.
Training often focused on livestock, especially pigs.
Austin Curtis, Sr., agricultural expert, instructs George Cox, a 13-year-old 4-H club member and son of a “renter” or tenant farmer, in pork nutrition near the West Virginia Collegiate Institute (near Charleston). / Photograph by Lewis W. Hine, on assignment for the National Child Labor Committee, October 10, 1921, from the Library of Congress.
Austin Curtis, Sr., conveyed the latest information about swine management to young people organized through local 4-H clubs. His son, Austin Curtis, Jr., participated in these efforts, raising a sow and tending her piglets as part of his pig project. This work helped stabilize farm incomes, a critical step in farm solvency for owners and tenant farm families. Bulletins like “How to Raise Pigs With Little Money” (1915), by George Washington Carver, facilitated this type of instruction.
Austin Curtis, Jr., 10 years old, participated in the pig clubs that his father, Director of Agriculture at West Virginia Collegiate Institute, helped organize. / Photograph by Lewis W. Hine, on assignment for the National Child Labor Committee, October 10, 1921, from the Library of Congress.
Austin Curtis, Jr., grew up immersed in Black land-grant networks, but alternatives existed. Carter G. Woodson (1875–1950), who held the position of Dean at the West Virginia Collegiate Institute between 1920 and 1922, proved that working in a West Virginia coal mine could lead to higher education. Woodson became the second Black man to earn a doctoral degree at Harvard University in 1912. He founded the Association for the Study of Negro Life and History (now the Association for the Study of African American Life and History) in 1915 and launched the Journal of Negro History (now the Journal of African American History) in 1916 to encourage Black and white scholars to study Black history. Woodson also launched Negro History Week (now Black History Month) in 1926 to facilitate exchange.
Curtis’s father took summer classes at Cornell University to remain current in livestock management. Ultimately, Curtis, Jr., selected Cornell University, too, and studied plant physiology there, earning his bachelor’s degree in 1932. After graduation he returned to West Virginia and worked in a greenhouse, for a landscaping business, and drove a cab, before accepting a teaching position at his father’s alma mater in Greensboro, North Carolina.
In 1935 Curtis, Jr., accepted a fellowship funded by the General Education Board to serve as George Washington Carver’s research assistant at Tuskegee Institute. He began work at Tuskegee in September 1935.
Tuskegee Institute football pennant, 1920–1950. / THF157606
Family Matters
As Austin Curtis, Jr., built his career as a chemist, he also pursued a personal life. While teaching at the A&T College in Greensboro, he met Belle Channing Tobias, head of biology at Bennett College for Women (now Bennett College). She was the daughter of Mary Pritchard and Channing Heggie Tobias, a minister, civil rights activist, and director of YMCA work among Black residents in New York City. The media reported on the Curtis-Tobias wedding as a society event held in St. Paul’s Chapel, Columbia University, New York City, on June 15, 1936.
Postcard, Marine Biological Laboratory, Woods Hole, Massachusetts, 1930–1945. / Wikimedia Commons
Described as “brilliant,” Tobias earned her bachelor’s degree at Barnard College, graduating Phi Beta Kappa. She studied zoology at Wellesley College and conducted research at the Marine Biological Laboratory in Woods Hole, Massachusetts. She was on leave from her faculty position at Bennett College and enrolled in the doctoral program at Columbia University at the time of her marriage.
Austin and Belle Curtis planned to honeymoon in West Virginia and then drive to Tuskegee Institute. Tragically, Belle fell ill from kidney disease during the honeymoon, and died at Mount Sinai Hospital in New York City on October 7, 1936, just four months after the wedding (“Death Claims Belle Tobias,” New York Amsterdam News, October 10, 1936).
Work with Carver consumed Curtis after his wife’s death. His loss coincided with the growth of chemurgy, a branch of chemistry dedicated to industrial uses of plant byproducts. Correspondence between Henry Ford and George W. Carver ensured that Carver (and Curtis) were well informed about industrialist Ford’s investment in chemurgy. This drew increased attention to their work.
Somehow Curtis found time to court Tuskegee Institute art teacher Oreta Adams (1905–1991). Her parents, King P. Adams (1870–1944) and Sarah Bibb Adams (1870–1944), lived in Lawrence, Kansas. Her father was a janitor at the University of Kansas in Lawrence, and a member of the Black Masons, an organization which supported leadership and service within Black neighborhoods. Curtis and Adams married at Adams’s parents’ home, 318 Locust Street in Lawrence, on August 3, 1938.
The Chicago Defender reported that the couple spent a week in Lawrence, then traveled through Illinois on their way back to Tuskegee, where they both resumed their posts. Their Illinois destination, in addition to Chicago, was the University of Illinois. This land-grant university was noted for soybean research. It had soybean experts on faculty and staff, and research in soybean genetics and in soybean uses ongoing. (“Kansas Girl Marries Aide to Dr. Carver,” Chicago Defender, August 13, 1938). Curtis also spent one summer working in the Soybean Laboratory in Greenfield Village. He stayed with his uncle, Cornelius S. Curtis, who lived in Detroit (Curtis Oral Interview, July 23, 1979, Benson Ford Research Center, The Henry Ford, page 31–32).
Curtis: Carver’s Support System
Curtis provided a lot of support to Carver over the years, including driving him to public engagements.
Between the death of Belle and his marriage to Oreta, Curtis drove Carver to Dearborn, Michigan. They participated in the third Dearborn Conference on Industry held in 1937. Curtis presented information on Carver’s products, including peanut and sweet potato extracts, and on his own chemical work, including isolating pigments from wild plants and devising uses for oil extracted from magnolias (“Tuskegee Chemist in Address at Detroit,” Chicago Defender, June 5, 1937).
Curtis and Carver also toured Greenfield Village. Carver described it as “one of the greatest educational projects I have ever seen” in a thank-you letter to Henry Ford, written on Dearborn Inn letterhead. One highlight was their interaction with Francis Jehl, a research assistant to Thomas Edison and an advisor on the lab reconstruction in Greenfield Village. On the drive back to Tuskegee, they stopped to visit the Curtis family in Institute, West Virginia (“Tuskegee Chemist in Address at Detroit,” Chicago Defender, June 5, 1937).
Left to right: Austin W. Curtis, George Washington Carver, William Simonds, and Francis Jehl at Menlo Park Laboratory, Greenfield Village, 1937. / THF213745
One of the most important services Curtis provided involved promoting Carver’s work at every opportunity. Sometimes this took the form of public speaking. During the ceremony that recognized Carver’s 40 years of service to Tuskegee Institute, Curtis delivered a ten-minute overview of Carver’s life and work, broadcast on WJDX radio (“To Unveil Bust of Dr. Carver June 2,” Chicago Defender, May 22, 1937).
Curtis claimed to have started the Carver Museum (now part of the National Park Service’s Tuskegee Institute National Historic Site) at Tuskegee. Installed on the third floor of the Institute’s library building initially, it featured Carver’s paintings, needlework, extracts, and other plant byproducts (Curtis Oral Interview, page 27). Carver toured Henry Ford through the museum during Ford’s first of three visits to the Tuskegee campus in March 1938. The group inspected peanut oil, which Carver promoted as part of massage therapy for infantile paralysis (“Ford Visits Tuskegee; Talks on Science with Dr. Carver,” Chicago Defender, March 19, 1938).
The museum received more attention as the relationship between Carver and Ford grew. In March 1941, during Ford’s third trip to Tuskegee, the group dedicated a new George Washington Carver Museum. Curtis helped a Tuskegee student insert soy-based plastic composite material into concrete blocks as part of the ceremonies.
George Washington Carver, Clara Ford, and Henry Ford at dedication of George Washington Carver Museum, March 1941. / THF213788
Cultivating Carver’s legacy took Curtis and Carver on the road regularly. Trips often consisted of multiple speaking engagements with Curtis assisting. Audiences ranged from children to peers equally invested in chemurgy research. The photo at the top of this post shows one of those appearances.
Curtis was never far from Carver, as photographs of Carver’s entourage attest. Curtis drove Carver, assisted him as he became more infirm, and looked out for his well-being during two events hosted by Henry Ford. The first, in March 1940, focused on the dedication of the George Washington Carver Elementary School in Richmond Hill, Georgia. Then, in July 1942, the two traveled to Henry Ford’s Edison Institute (now The Henry Ford) in Dearborn, Michigan, for the dedication of the Carver Nutrition Laboratory and the Carver Memorial (now the George Washington Carver Cabin) in Greenfield Village.
Curtis urged Carver to leave a legacy. This took the form of an endowment to carry on Carver’s work. The media reported on formation of the George W. Carver Foundation during the 15th Negro History Week celebration, which occurred February 11–17, 1940 (“This Day in History,” Chicago Tribune, February 14, 1946).
A gentleman’s agreement of a sort apparently existed between Curtis and Carver. Curtis fully expected to continue Carver’s work, and he informed Henry Ford of that fact in a January 1943 letter. Tuskegee president F.D. Patterson had other ideas. The two disagreed over royalties specified in a publishing contract, and the Tuskegee board terminated Curtis in April 1944 (“Aide to Dr. Carver Eased Out at Tuskegee,” Atlanta Daily World, April 22, 1944). By that time, the book, George Washington Carver: An American Biography (Doubleday, Doran & Co., 1943), was selling well, and Carver’s contract with the publisher had guaranteed Curtis a percentage of the royalties.
Curtis after Tuskegee
Curtis pivoted rapidly after his firing. He had to. His wife, Oreta, had just given birth to their first child, Kyra. He had relatives in Detroit, and his association with Henry Ford and awareness of chemurgy networks likely drew him to the city. He launched A.W. Curtis Laboratories to manufacture health care products and cooking oil derived from Carver’s research. The Curtises’ second child, daughter Synka, was born in Detroit in 1946.
Curtis Rubbing Oil, circa 1987, for fast relief of minor aches and pains of arthritis and rheumatism. The back of the bottle describes best uses and warnings for children. The active ingredients are listed as "Peanut Oil, Methyl Salicylate.” / THF170781
Product marketing stressed Curtis’ connection to Carver. A. W. Curtis Laboratories held the grand opening of its sales office on National Carver Day, January 4, 1947 (he had died on January 5, 1943). The Detroit Tribune advertisement included a photograph of Carver and Curtis at work together in their Tuskegee laboratory and the oft-quoted phrase attributed to Carver: “through [Curtis] I see an Extension of my Work.” Curtis also arranged for Rackham Holt, author of George Washington Carver: An American Biography, to be available to sign books. To sweeten the prospects of a sales-office visit, Curtis offered three prizes for ticket holders, including one-half gallon of “our Peanut Cooking Oil” (January 4, 1947, page 8).
Austin Curtis, Jr., remained in touch with The Henry Ford, off and on, during his years in Detroit. He conducted an interview with Doug Bakken and Dave Click in 1979. Curtis visited Greenfield Village on August 17, 1982, to reminisce about the dedication ceremony that had occurred 40 years before.
Austin W. Curtis visiting the George Washington Carver Cabin in Greenfield Village, August 17, 1982. / THF287706
Curtis helped expand The Henry Ford’s collection of Carver items by offering, in 1997, a microscope and typewriter used by Carver at Tuskegee. By then, Curtis was also reducing his involvement in his business. The Reverend Bennie L. Thayer, chairman of the board for Natural Health Options, Inc. acquired A.W. Curtis Laboratories in 1999, and the next year, Dr. E. Faye Williams purchased the company and manufacturing rights. Curtis died in Culver City, California, on November 5, 2004.
Notes about Sources
Much remains to learn about Curtis’s life in Detroit. Consult the Austin W. Curtis Papers, 1896–1971, at the Bentley Historical Library, University of Michigan, for more.
Newspaper articles mentioned Curtis in coverage of Carver through the years they worked together (and beyond). Newspaper accounts of Curtis, Jr., provided leads to follow. These appeared in the Chicago Defender (Arnold De Mille, January 29, 1955) and the New York Amsterdam News (Julian Jingles, February 24, 1996, and Herb Boyd, October 9, 2014).
Ancestry.com confirmed genealogical details. Newspapers articles affirmed events (as referenced throughout the text).
Secondary sources documenting Curtis, Sr., and Jr. and West Virginia history include:
Askins, John. “Austin W. Curtis, Jr.: He Lives in Shadow of G. W. Carver,” Biography News (May/June 1975), pg. 511.
“Austin Wingate Curtis [1872-1950],” History of the American Negro. West Virginia Edition. A. B. Caldwell, editor. Vol. 7. Atlanta, Georgia: A. B. Caldwell Publishing Company, 1923.
Moon, Elaine Latzman. “Austin W. Curtis, [Jr.,] D.S.C.” in Untold Tales, Unsung Heroes: An Oral History of Detroit’s African American Community, 1918–1967. Detroit: Wayne State University Press, 1994, pp. 253-255.
Morgan, B.S., and J.F. Cork. “Beginning of West Virginia State University.” History of Education in West Virginia. Charleston: Moses W. Donnally, 1893, pp. 189-94.
Turner, Ruby M. “The Life and Times of Dr. Austin Wingate Curtis, Jr.,” Simpson College Archives, Indianola, Iowa.
Debra A. Reid is Curator of Agriculture and the Environment at The Henry Ford. Saige Jedele and Sophia Kloc shared comments that improved this blog.
entrepreneurship, agriculture, Michigan, Detroit, education, by Debra A. Reid, George Washington Carver, African American history
 Paul Foster storing bread in the Soybean Laboratory in Greenfield Village, Dearborn, Michigan, circa 1935. / THF236481
Paul Foster storing bread in the Soybean Laboratory in Greenfield Village, Dearborn, Michigan, circa 1935. / THF236481
The Soybean Laboratory (now the Soybean Lab Agricultural Gallery) in Greenfield Village buzzed with activity during the 1930s and 1940s. Paul Hunter Foster worked as a waiter in that laboratory in its earliest days, but over time, his responsibilities expanded to include valet to Henry Ford and cook on Henry Ford’s private railroad car, Fair Lane. As these photographs indicate, he tested soy foods and may have fed the laboratory staff in the process.
Paul Hunter Foster was born on June 5, 1900, to a well-connected mixed-race family living in Meridian, Mississippi. His father, William Thomas Foster, sampled cotton and rated bales based on cotton quality. His mother, Alvina (“Vinie”/“Viny”) Lewis Hunter, bore seven and raised five children. Most of them pursued higher education and community service and flourished professionally. Three studied at Tougaloo College in Jackson, Mississippi. One graduated from Fisk University in Nashville, Tennessee, and another from Howard University in Washington, D.C. Two of Paul’s brothers became dentists, and another worked in race relations throughout his career.
Piecing together the details of Paul Foster’s life remains a work in progress, but primary sources confirm that he lived in Washington, D.C., after his father died in 1917. One of his brothers lived there at the time, attending Howard University. Paul worked as a messenger for the U.S. War Department during World War I (per his draft registration card). He was back in Meridian in January 1920 (per the U.S. Census). Then, on July 7, 1920, while still a student, he married Lilybel E. Scott in Detroit, and settled into life at 6081 Whitewood Avenue in Detroit.
Lilybel Scott Foster (left) with Paul Hunter Foster (right) and Georgia Singleton Ralls (center) of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, during the dedication of the Stephen Foster Home (now the Sounds of America Gallery/Foster Memorial) in Greenfield Village, July 4, 1935. / THF272761
It remains unclear when Paul Foster joined Henry Ford’s staff, but his work in Greenfield Village and in proximity to Henry Ford’s office at Ford Motor Company’s Oakwood Boulevard headquarters translated into “other duties as assigned.” In 1935, this included escorting a special guest invited to the Stephen Foster Home dedication. A reporter from the Pittsburgh Courier explained on September 21, 1935, that Georgia Singleton Ralls had, as a child, lived in the house in Lawrenceville, Pennsylvania. She provided valuable information about the home interior to Henry Ford via Charles T. Newton. Ford invited her, but the Foster family ensured her personal comfort. She stayed with Paul and Lilybel and their four children during her visit. Ralls described Paul Foster as Henry Ford’s valet.
Detroit newspapers confirm that Paul and Lilybel Foster encouraged education, a love of music and theater, and civic engagement. Lilybel and the four children, Paul H. Foster, Jr., [William] Estus, Jane, and Harris, each received their share of coverage in the Michigan Chronicle social pages. This helped them forge networks with other middle-class Black Detroiters.
In addition, Paul Foster, Sr., developed relationships with other Black Detroiters working in industry. His eldest child, Paul, Jr., listed Bohn Aluminum as his employer on his World War II draft registration card, and his second son, William Estus, listed Ford Motor Company. The elder Foster also listed Ford Motor Company, Oakwood Boulevard, as his employer. The sons listed their mother as the person most likely to know their permanent addresses, but Paul, Sr., listed Frank Davis, a field agent for Detroit Light Company (Detroit Edison Company), instead of his wife. This likely reflected a commitment to class and racial bonds among well-connected Black Detroiters employed in managerial positions by white business owner-operators. Frank Dewitt Davis became the first Black employee in an office position at Detroit Edison according to his obituary (published in the Detroit Free Press, September 19, 1974).
Work in the Soybean Lab
The following provides a snapshot of the chemical laboratory that Henry Ford constructed in Greenfield Village during 1929, and the workspace that Paul Hunter Foster, Sr., occupied.
Henry Ford invested in the chemical laboratory to discover industrial uses of agricultural products. Soybeans, a crop with a long history, became the research focus by 1931. The crop offered much potential. Extracted oil could be refined for multiple uses and the bean residue could be pressed into numerous molded forms. The protein- and oil-rich soybean also addressed the need of many seeking healthier foodstuffs.
Chemical Laboratory in Greenfield Village, 1930 (today known as the Soybean Lab Agricultural Gallery). / THF222341
Foster worked in the lab that undertook food experiments during this early period of exploration and innovation. His workspace consisted of the low-roofed kitchen shown below, divided by a railing. The preparation area included ingredients, storage containers, scales and other data collection instruments, and scientific apparatuses to facilitate testing.
Preparation and testing area of the kitchen laboratory at the Soybean Laboratory in Greenfield Village, Dearborn, Michigan, circa 1935. / THF236497
Staff worked together in this testing kitchen. The photograph below shows Foster at work in the foreground, and another lab technician busy in the background.
Paul Foster making soybean bread inside the Soybean Laboratory in Greenfield Village, Dearborn, Michigan, circa 1935. / THF236493
The cooking area in the kitchen laboratory included a range, a sink, and counter space, as well as measuring cups, pots, pans, and other kitchen implements. It was at a slightly lower level than the preparation area.
Making soybean bread in the Soybean Laboratory in Greenfield Village, Dearborn, Michigan, circa 1935. / THF236485
Food testing occurred in this lab. The results appeared in the booklet “Recipes for Soybean Foods.” It described the work of the laboratory, summarized the benefits of soy-based foods, and consolidated recipes proven in this laboratory.
“Recipes for Soybean Foods,” circa 1931. / THF119278
Cooks had to be aware that preparing soybeans required some extra effort. For example, “the soy bean generally requires a longer time for cooking than does the common bean…. With a pressure cooker, the beans can be cooked in 20 minutes at 20 pounds pressure” (page 2). Paul Foster used a pressure cooker to prepare soybeans in the kitchen workspace.
Lab technician (likely Paul Foster) with a pressure cooker in the Soybean Laboratory in Greenfield Village, circa 1935. / THF236489
Soybeans had a higher protein content than navy beans or lima beans, according to “Recipes for Soybean Foods.” Thus, cooks substituted soybeans to facilitate healthy eating.
An omelette, two baked beans recipes, and two salad recipes in “Recipes for Soybean Foods,” circa 1931, page 9. / THF119283b
Soy flour also offered a higher-protein alternative to wheat flour, and a flour more supportive of diabetic diets and other diets for those intolerant to certain foods. Furthermore, soy flour properties helped bread remain fresher for longer. As “Recipes for Soybean Foods” explains, breads that incorporated 5% soy flour and 95% wheat flour produced a loaf of bread that kept longer than bread made without soy flour. Combining flours at a ratio of 20% soy and 80% wheat resulted in a bread loaf with 40% more protein than wheat flour alone (page 2). Such persuasive arguments converted some to soy.
The photographic print below shows Paul Foster preparing dough for soybean bread in the kitchen workspace.
Making soybean bread inside the Soybean Laboratory in Greenfield Village, Dearborn, Michigan, circa 1935. / THF236491
After baking, storing the bread in a wire-enclosed wood-frame container was the next step in the longer process of documenting drying rates for different types of bread loaves.
Storing bread in the Soybean Laboratory in Greenfield Village, Dearborn, Michigan, circa 1935. / THF236483
A closer look at Foster and his bread loaves, in the photo at the very top of this post, shows him in the process of loading the loaves into the food safe (a term used for similar wire-sided storage cabinets). The experiments in the test kitchen continued with rotation of loaves and measuring rates of dryness.
Interested in trying the recipe for the soybean bread baked in the laboratory in Greenfield Village? Check out page 4 of Recipes for Soybean Foods, or explore these and other recipes in the Ford Motor Company bulletin, published around 1939 (and two pages longer). Be mindful of inconsistencies. In both, on page 2, the directions indicate that the pressure cooker should be set at 20 pounds pressure, but page 16 in the earlier booklet, and page 18 in the 1939 version, states that soybeans should be cooked for 20 minutes at 25 pounds.
“Recipes for Soy Bean Foods,” Ford Motor Company, circa 1939. / THF223249
Foster remained visible in Soybean Laboratory research through the visit of George Washington Carver in July 1942. During this visit, Henry Ford dedicated a nutrition laboratory on Michigan Avenue, adjacent to Greenfield Village, named for Carver. It included an experimental kitchen described as “the dominion of Mr. Paul Foster” (Herald, August 14, 1942, page 12).
George Washington Carver (seated) at the dedication of Carver Nutrition Laboratory, Dearborn, Michigan, July 21, 1942. Paul Foster is standing in the foreground to the right. / THF214097
Foster apparently had full authority over the kitchen in the Carver Nutrition Laboratory: “Here this master of the culinary art will hold forth, concocting delicious morsels” (Herald, page 12). Carver credited Foster with the “weed sandwiches” sampled during the Nutrition Lab dedication (Herald, page 14). Carver appreciated such ingenuity, given his recent bulletin Nature’s Garden for Victory and Peace (March 1942). Foster’s sandwich spread of “nature’s vegetables” consisted of ground dandelion, purslane, curly dock, plantain, chickweed, lamb’s quarters, bergamot, oxalis, and radish seed pods with salt, lemon juice, and mayonnaise added. Served on soybean bread, such a mixture could have a wonderful flavor and “contain the equivalent in vitamins and minerals to the average person’s monthly diet of vegetables.” So explained Edison Institute student Robert Cavanaugh, who reported on “The Development of a New Laboratory” (Herald, page 12). A photograph of Foster, preparing vegetable sandwiches, illustrated the story.
Documenting Paul Foster’s role in research in either laboratory after 1942 remains a work in progress. Consider this a first installment as we continue to learn more about the scientists who worked at the Soybean Laboratory in Greenfield Village, and at the nearby Carver Nutrition Laboratory on Michigan Avenue.
Debra A. Reid is Curator of Agriculture and the Environment at The Henry Ford. She thanks Saige Jedele and Sophia Kloc for feedback that improved this blog.
Washington DC, 1940s, 1930s, 20th century, soybeans, research, recipes, Michigan, Henry Ford, Greenfield Village buildings, Greenfield Village, food, Detroit, Dearborn, by Debra A. Reid, African American history
Cast in Plaster: Isaac Hathaway and Sculpture as Black Biography
Black sculptor Isaac Scott Hathaway (1872–1967) took issue with inadequate recognition of Black achievement. He dedicated his career to creating and marketing affordable plaster busts and other commemorative sculpture, literally putting Black activists, educators, ministers, and dozens of other individuals on a pedestal. These stood in stark contrast to lawn jockeys and other statuary that emphasized caricatures and stereotypes.
Plaster Plaque of George Washington Carver (1864?–1943) Cast by Isaac Scott Hathaway, 1945. / THF152082
Hathaway remembered visiting a Midwestern museum when he was nine years old (around 1881), with his father, Robert Elijah Hathaway (1842–1923). The young Hathaway wondered why museums did not include statues of Black people. His father explained that white people modeled their own, and that if Black Americans wanted to see sculptures of Black Americans, “we will have to grow our own sculptors.”
This museum visit changed Hathaway’s life, as he recalled in a 1939 Federal Writers’ Project interview and in a 1958 article in the Negro History Bulletin. He studied art during the era of the New Negro, a movement of the 1890s to 1910s that emphasized African and Black American contributions to the arts, literature, and culture. He taught school, created sculpture, and distributed his plaster casts through the Afro Art Company, which he launched after he moved to Washington, D.C., in 1907.
Hathaway moved when opportunities to further ceramics education arose. He relocated to Pine Bluff, Arkansas, by 1915 to launch ceramics education at the Branch Normal College (now the University of Arkansas at Pine Bluff). He moved his company, renamed the Isaac Hathaway Art Company, to Pine Bluff at the same time. In 1937, he joined the faculty at Tuskegee Institute (now Tuskegee University) in Alabama, to introduce a ceramics curriculum there. In 1947, he moved to Montgomery, Alabama, to direct ceramics instruction at Alabama State College (now Alabama State University).
Plaster Cast of George Washington Carver's Hand, 1943. / THF34092
The Henry Ford has two of Hathaway’s plaster casts. Hathaway gave them to Henry Ford in December 1945, explaining that he wanted Ford to have the small plaque (shown at the beginning of this post) and “a cast … made from the hand of the late Dr. George Washington Carver” (shown above). The plaque was one of three types of casts of Carver that Hathaway made. The others included a small bust (around one foot tall) and a heroic bust, visible in this photograph of the artist at work (courtesy of the Tuskegee University Archives).
Carver’s hands attracted a lot of attention, long and strong and well-worn after years of physical labor. Based on Hathaway’s description, it appears that he made the cast of Carver’s hand after Carver died on January 5, 1943. Hathaway instructed students in techniques he used. Photographs show him instructing students in creating molds of their hands at Alabama Polytechnic University (now Auburn University) around 1947.
Hathaway’s reputation earned him a commission in 1946 to design the Booker T. Washington Memorial Half Dollar. This was the first coin designed by a Black American for the U.S. Mint, and the first coin minted that featured a Black American. You can read more about this in “Coining Liberty: The Challenge of Commemorating Black History.”
Hathaway’s plaster casts remind us of the importance of acknowledging Black accomplishments. Others followed his examples.
Benjamin Akines (c1904–?), a bricklayer and brick mason living in Jackson, Mississippi, knew of Henry Ford’s interest in and respect for Carver’s work. Akines gave Ford a bust of the Black scientist in 1941, four years before Hathaway sent his two casts to Ford.
Bust of George Washington Carver, circa 1941. / THF170783
Akines sent the plaster bust and a letter directly to Henry Ford: “Enclosed you will find a token (in the form of a bust) of one of whom I am told you esteem very highly … I trust this will mean a moment of happiness to you.” Akines claimed that he “was divinely inspired to model,” though he worked as a bricklayer. The back of the bust represents the work of a bricklayer, sculpted with a cut stone foundation with a laid brick pier. This brickwork was his signature, as Akines included bricks in other creative works. On November 10, 1931, he received a patent for an ornamental clock case in the form of a brick façade and sides (Patent Des. 85,507).
Bust of George Washington Carver, circa 1941, Cast by Benjamin Akines. / THF170784
Eager to share his efforts, Akines communicated his news to the Chicago Defender, the Black newspaper in the then second-largest U.S. city, Chicago, Illinois. It reported that “Akines, a bricklayer who indulges in sculpturing as a hobby,” gave Ford a plaster cast of Carver, and that Ford’s secretary and Carver himself acknowledged his generosity (“Bricklayer-Sculpturor [sic] is Lauded for Bust of Carver,” July 12, 1941).
It is difficult to know whether others who cast busts of Carver influenced Akines’ approach. For example, German-born Steffen Thomas (1906–1990) sculpted a clay model of Carver during a 1936 visit to Tuskegee. This was the model from which he cast the sculpture recognizing Carver’s 40 years of service to Tuskegee. The gift received media coverage at the time Carver received it in 1937 and appeared prominently during the dedication of the Carver Museum in 1941, given its location on a plinth outside the museum.
George Washington Carver and Austin W. Curtis, Jr., at Tuskegee Institute with Sculpture by Steffen Thomas, circa 1938. / THF213732
These last two examples indicate more recent commemorations of Black historical figures. One represents a respectful but commercial venture, and the other an exceptional recognition.
Commemorative Bust of Rosa Parks (1913–2005), designed by Sarah’s Attic, Inc., 1995. / THF98391
A popular Michigan-based figurine manufacturer, Sarah’s Attic., Inc., released a limited-edition bust of rights activist Rosa Parks in 1995. Cast of synthetic resin and hand-painted, it was one of four “Faces of Courage” in the Black Heritage Collection. The others featured abolitionist Harriet Tubman, a Buffalo Soldier, and a Tuskegee Airman. The Rosa Parks bust was one of 9,898 made and distributed through a commercial contract, with Sarah’s Attic holding the copyright and Rosa Parks holding the license.
Commemorative Bust of Detroit Lions Tight End Charlie Sanders (1946–2015), 2007. / THF165543
This cast metal bust of the Detroit Lions’ legendary tight end Charlie Sanders exists because of his election to the Pro Football Hall of Fame. The Hall commissioned Tuck Langland, an artist and retired university educator, to cast Sanders. Langland first created a bust out of clay based on photographs and a visit with Sanders. That clay statue became the model for the cast bronze bust displayed in the Hall of Fame Gallery in Canton, Ohio, and the copy presented to Sanders (and later donated to The Henry Ford).
So many variables exist in the business of commemoration.
When Isaac Scott Hathaway created respectful sculptures of Black Americans, he challenged white exceptionalism. Who decided who received recognition? Hathaway. What criteria informed his decisions? He selected subjects he respected, but as an educator, he selected people with lessons to teach, and as a businessman, he selected subjects that would sell. Disagreements over selections can derail seemingly straightforward acknowledgment.
What form should the recognition take? Hathaway mass-produced inexpensive plaster casts. Others create one-of-a-kind sculpture or mass-produce limited-edition items. Other recognition in the form of a historical marker or a street sign can draw attention to places of significance and the people who lived there.
Recognition of Black accomplishments remains important—in fact, critical—to understanding the human experience.
Sources
Gates, Henry Louis, Jr. “The New Negro and the Black Image: From Booker T. Washington to Alain Locke.” Freedom’s Story, TeacherServe©. National Humanities Center.
“The Hathaway Family: A Journey from Slavery to Civil Rights,” a paper compiled by scholars Yvonne Giles, Reinette Jones, Henri Linton, Brian McDade, Quantia "Key" M. Fletcher, and Mark Wilson, based in materials at these institutions: Alabama State University, Montgomery, Alabama; Auburn University, Auburn, Alabama; the Isaac Scott Hathaway Museum, Lexington, Kentucky; the Mosaic Templars Cultural Center, Little Rock, Arkansas; Tuskegee University Archives, Tuskegee, Alabama; the University Museum and Cultural Center, University of Arkansas Pine Bluff, Pine Bluff, Arkansas. (n.d.).
“Isaac Scott Hathaway,” a product of the Appalachian Teaching Project, Auburn University, and the Tuskegee Human and Civil Rights Multicultural Center (2012).
"Isaac Scott Hathaway: Artist and Teacher," Negro History Bulletin, vol. 21, no. 4 (January 1958), pp. 74, 78-81.
Perry, Rhussus L. Federal Writers’ Project Interview of Isaac Hathaway. February 2, 1939. Folder 60, Coll. 03709, Federal Writers' Project papers, Southern Historical Collection, The Wilson Library, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
Register, Heather. “Isaac Scott Hathaway (1872-1967).” Encyclopedia of Arkansas.
Zinkula, Jacob. “South Bend Artist Busts His Way into Football Hall of Fame.” South Bend Tribune. 13 July 2015.
Debra A. Reid is Curator of Agriculture and the Environment at The Henry Ford, and sends appreciation to Saige Jedele and Sophia Kloc for comments that strengthened this post.
teachers and teaching, education, making, George Washington Carver, Rosa Parks, by Debra A. Reid, art, African American history
Crispus Attucks and Evolving Perceptions of the Boston Massacre
 “The Bloody Massacre,” 1770, engraved by Paul Revere and hand-colored by Christian Remick. / THF8141
“The Bloody Massacre,” 1770, engraved by Paul Revere and hand-colored by Christian Remick. / THF8141On March 5, 1770, in King Street in Boston, Massachusetts, several British soldiers fired into an angry group of civilians who had been taunting them. When the shooting was over, five of these civilians lay dead or dying. The first to fall, it is believed, was a man of African American and Native American heritage named Crispus Attucks.
The event, which soon became known as the Bloody Massacre, or—over time—the Boston Massacre, incensed Bostonians to such an extent that it came to be considered a defining moment in the lead-up to the American Revolution.
The more than 200 eyewitness accounts that were collected afterward agreed on some points but disagreed on many others. In the end, we have only impressions, fragments, and often competing narratives of what people remembered seeing. The sequence of events might have gone something like this: The initial angered group approached a guard in front of the Customs House and started insulting him and pelting him with snowballs and chunks of ice. The situation quickly escalated as the crowd grew larger. The guard called for reinforcements. Other British soldiers, including a captain, arrived. More townspeople joined in, throwing snowballs and insults at the troops. A soldier was knocked to the ground. He stood up, yelled, and fired his musket into the crowd. Then several other soldiers fired their weapons, killing three and mortally wounding two others.
Perhaps this is the sequence of events. We will never know for sure.
Whatever people thought they saw, almost immediately the popular press took full advantage, describing the event in endless detail and hailing the fallen victims as martyrs in the fight for liberty. Even the use of the word “massacre” implied a premeditated, cold-blooded, intentional act by British soldiers against American patriots.
This event did not occur in isolation but was an outgrowth of months of increasing tension between the British and Boston civilians, who were angered by the relentless passage of new British-imposed taxation laws. In 1768, British soldiers had been deployed to Boston to try to maintain order there.

“A View of Part of the Town of Boston in New-England and British Ships of War Landing Their Troops!” 1768, engraved by Paul Revere and hand-colored by Christian Remick. / THF11644
In fact, the angry individuals who had initially taunted the soldiers were not patriotic Sons of Liberty but working-class day laborers, apprentices, and merchant sailors. These individuals had a particularly personal gripe against the British soldiers: the soldiers, who were poorly paid, often competed with them for jobs, and this competition inevitably led to lowered wages.
In the end, it didn’t matter that the initial crowd who started the fracas was motivated more by economic reasons (jobs, wages) than ideological ones (liberty, independence). Nor did it matter that John Adams’ brilliant defense of the soldiers eight months later in court played to the jury’s prejudices against race and class by labeling the angry crowd as an unruly mob of young, lower-class, Black and Irish sailors. Bostonians were riled up. And the fact that all but two soldiers were acquitted at the end of their murder trial further inflamed them.

Engraving of “The Bloody Massacre,” created about 1800 from the original 1770 Paul Revere print, showing a clearer depiction of the Butcher’s Hall sign than the hand-colored lithograph shown at the beginning of this post. / THF130817
One Boston patriot, engraver Paul Revere, decided to use this event to make a larger political statement (for more on Paul Revere, see “Paul Revere and The Henry Ford's Tie to Tea”). Basing his engraving upon an as-yet-unpublished rendering created by artist Henry Pelham, Revere was able to complete his own engraving ahead of Pelham’s and start disseminating a mere three weeks after the event. He gave it the dramatic title, “The Bloody Massacre: Perpetrated in King Street, Boston on March 5, 1770, by a party of the 29th Regt.” This title ensured that the focus would be on the shooting, the place, and particularly on the “guilty”—i.e., the soldiers.
Revere cleverly heightened other details to make certain points—the orderly lineup of British soldiers firing into the American crowd, their actions depicted as brutal and deliberate; the colonists dressed as gentlemen rather than laborers, their behavior seen as innocent and defenseless; and, above the soldiers’ heads, a sign reading “Butcher’s Hall,” rather than the actual Customs House, to underscore the goriness of the event. All of these details—and more—were, in fact, inaccurate and misleading. But they certainly shaped public opinion. The narrative told within this print would endure for centuries—even to the present day. It was possibly the most effective piece of war propaganda in American history.
Noticeably absent in Paul Revere’s engraving is the aforementioned Crispus Attucks—generally thought to be the first casualty of the Boston Massacre. The reason for this? Likely, depicting a mixed-race, working class, itinerant sailor from out of town would not have played to the public sentiment that Revere was aiming for. Only later did Attucks emerge as the most famous of the five victims of the Boston Massacre.
What do we know about Crispus Attucks? Admittedly, not much. Historians believe he was born of an enslaved African American father and a Native American mother. He spent his early life enslaved to a man in Framingham, Massachusetts. At age 27, it is believed, he ran away (about 20 years before the Boston Massacre) and was never apprehended (he might have changed his name to avoid detection). An ad for a runaway slave that was possibly Attucks described him as 6’2”, with short, curly hair and a robust physique.
He apparently made his way to Boston, where he sought work as a sailor (one of the few trades open to non-whites), spending most of his time on whaling ships, and when on land, was a rope-maker (a typical dockside job for sailors). He was often at sea, and on this particular day, March 5, 1770, he was waiting for an opportunity to ship out. Not only could his anger at the British soldiers have been due to job competition, but he, like other merchant sailors, also faced the danger of being forcibly impressed into the British Royal Navy (for more on the lives and risks of African American merchant seamen, see “Piecing Together Black History: A Case Study”).
Accounts vary widely as to Attucks’ role in the Boston Massacre. Was he a leader and instigator of the angry crowd, as some claimed? Did he step into the fray, swinging a stick and grabbing a soldier’s bayonet, as others described? In defending the British soldiers, John Adams sought to distance Attucks (and the other so-called “rabble-rousers”) from the upstanding, respectable, solid citizenry of Boston. He described Attucks’ behavior as “mad” and declared him the self-appointed leader, chief to blame for the “dreadful carnage.” Other testimonies claimed he was not the leader or an instigator, but stood off to the side, watching the melee unfold. Rather than angrily wielding a stick, he was quietly leaning on one.
Most people at the time considered him—along with the other fallen victims—a martyr, a hero. Breaking with usual segregation customs, Attucks was accorded an honored burial alongside his fallen comrades at the Granary Burying Ground on Tremont Street. Burial rites for the victims, held at Faneuil Hall days later, reportedly attracted some 10,000 of Boston’s 16,000 citizens.

When seen through a special viewer, the two pictures in this stereograph give a three-dimensional effect. This circa 1859 stereograph is of Faneuil Hall, the public meeting hall that was the site of the burial rites for the Boston Massacre victims back in 1770. / THF278882
Several decades later, Attucks was recast as the central figure of the conflict. During the decades before the Civil War, anti-slavery advocates memorialized him in order to garner support to end slavery—calling him the first martyr in the fight for American independence.

The anti-slavery press, centered in northern states like New York and Massachusetts, produced and sold almanacs like this one that featured provocative cover illustrations depicting the brutality of slavery. / THF7209
In 1855, in direct contrast to Revere’s earlier engraving, artist William L. Champney featured Attucks in a brand-new rendering of the Boston Massacre, placing him at the very center of the conflict. The rendering was turned into a popular color print by J. H. Bufford.
In 1888, a monument (still standing today) was unveiled in Boston Common honoring all five victims of the massacre, but it focused attention on Attucks and was ever after referred to as the Crispus Attucks Monument. During the Civil Rights movement of the 1950s–1960s, Attucks became a powerful symbol of African Americans’ struggle for freedom and equality. In his seminal 1964 book Why We Can’t Wait, the Reverend Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. reinforced the symbolic role of Crispus Attucks:
He is one of the most important figures in African-American history, not for what he did for his own race but for what he did for all oppressed people everywhere. He is a reminder that the African-American heritage is not only African but American and it is a heritage that begins with the beginning of America.

Cover of Dr. Martin Luther King’s 1964 book, which contains the reference to Crispus Attucks. / THF266487
In recent years, Attucks’ role in the Boston Massacre has been reimagined again, this time as the first African American victim of unrestrained police brutality.
The role that Crispus Attucks played in this event was debated from the beginning. Was he the leader of an unruly mob angry about jobs? Was he a hero and a martyr, fighting for liberty? In fact, his most important role may be that of showing how perceptions of individuals can change over time. As historians and curators continue to sift through the documented details about the Boston Massacre, interpretations will change. But the power of this dramatic event, and the meaning people find within it, will endure.
Donna R. Braden is Senior Curator and Curator of Public Life at The Henry Ford. This blog post is part of a series that sheds new light on stories told within the With Liberty & Justice for All exhibition in Henry Ford Museum of American Innovation.
African American history, Henry Ford Museum, by Donna R. Braden
Quiet & Loud Protest

Photo by Curatorial Staff of The Henry Ford
When you think of the word “protest,” what does it mean to you?
- Marching at a rally with a sign?
- Participating in a “walk out” at school?
- Boycotting companies?
- Wearing a shirt or hat with a message?
- Correcting people on their biases?
- Donating money to organizations?
- Civil disobedience?
A new temporary exhibit now on view in Henry Ford Museum of American Innovation, Quiet & Loud Protest, explores this question by demonstrating the ways that protest can be both loud and quiet. Throughout history, people have found different ways to advocate for change, whether marching in the streets or finding quieter ways to be an ally. Both are valuable in drawing attention to injustices. The exhibit draws together a small selection of recent acquisitions that showcase how artist-activists have used graphics to demand change and organize communities. The content of the exhibition is replicated in this post (with slightly expanded descriptions) for those unable to see it in person.
Amos Paul Kennedy, Jr.


Amos Paul Kennedy Jr. has generously donated several prints to the collections of The Henry Ford. These examples feature quotes attributed to George Washington Carver and Rosa Parks—two advocates for change who are prominent in our collections. / THF626953 (top), THF626939 (bottom)
These letterpress prints are by Amos Paul Kennedy, Jr., who relocated to Michigan from the South in 1963 with his parents. In junior high, he experienced racism from teachers who presumed he was uneducated and poor because he was Black.
At the age of 40, Kennedy visited Colonial Williamsburg while on vacation with his family and was so enamored with the letterpress and bookbinding demonstrations being given by historical reenactors that he went home and began to take classes at a community print shop. His love for the medium grew to the point where he made the decision to leave his career as a corporate computer programmer at AT&T so that he could focus on printmaking full time.

Letterpress prints by Amos Paul Kennedy, Jr./ THF626947 (top), THF626949 (bottom)
He went on to earn an MFA in Fine Arts and taught in university art programs. When Kennedy left academia, he adopted the historical role of an iterant printer, travelling through the American South to different print shops, learning about print media and developing his style over the course of many years. Kennedy sometimes describes himself as a “humble Negro printer” and wears bib overalls with a pink dress shirt. By doing this, Kennedy confronts people with their biases, causing them to question race, language use, and class. In 2013, Kennedy moved to Detroit, where he operates Kennedy Prints today.

Letterpress prints by Amos Paul Kennedy, Jr. / THF626943 (top), THF626941 (bottom)
Kennedy is known for his prolific output of vibrant letterpress prints that address cultural biases and social justice issues. Many of his prints feature quotes by Black civil rights activists and abolitionists, scientists and innovators, and literary figures, as well as traditional African proverbs. In an interview with the Library of Congress in January 2020, Kennedy said:
“People sometimes classify me as a political artist, and I find that amusing because when I was young, I was told that everything you do is political […] I print the things that reflect the way that I want the world to be. I think that people who say they are not political in their work fail to recognize that ‘not being political’ is a political act.”
Kennedy refuses to call himself an artist and sells his work at affordable prices to make it more accessible. Thanks to the power of the multiple, Kennedy can use printmaking to spread messages of hope widely—to reflect exactly the type of world that he wants to live in.
Corita Kent

Photo by Kristen Gallerneaux
Many people imagine the life of a Catholic nun as quiet and contemplative. Sister Mary Corita Kent challenged this notion. In 1936, after graduating high school, she joined the Order of the Immaculate Heart of Mary—a progressive Catholic convent and college in Los Angeles—where she taught art until 1968.
In the mid-1960s, Corita became famous for her colorful screenprints inspired by social justice issues, religious scripture, advertising, popular music, and literature. Her most celebrated prints are text-heavy and vibrant, layering blocks of bright color and DayGlo ink with high-key photographic imagery and words that twist around the page.
Detail of Quiet & Loud Protest exhibit with Corita Kent’s “my people” print. / Photo by Kristen Gallerneaux
Her print “my people” pairs a newspaper clipping about the 1965 Watts Uprising with a quote from Maurice Ouellet, an outspoken priest involved in the Civil Rights Movement in Selma, Alabama. Part of the quote Corita included reads: “Youth is a time of rebellion. Rather than squelch the rebellion, we might better enlist the rebels to join that greatest rebel of his time—Christ himself.” And in an oral history, Corita herself said: “I feel that the time for physically tearing things down is over. It’s over because as we stand and listen, we can hear it crumbling from within.”
Corita Kent’s print “You Shoot at Yourself, America” was created in response to the 1968 assassination of Robert F. Kennedy. It features a poem by Yevgeny Aleksandrovich. / THF189649
Corita Kent’s print “Road Signs (Part 1 & 2)” features text excerpted from Walt Whitman’s Leaves of Grass. / THF189650
Corita encouraged collaboration and “presence” among her students and encouraged them to balance awareness of political issues with finding joyful moments—even during dark times. Many important designers and creative thinkers visited her classroom, including Buckminster Fuller and Charles and Ray Eames. Artist Ben Shahn once called her “a joyous revolutionary” and in the media she was styled as a radical “pop art nun.”
Art was a Corita’s way of protesting through LOUD colors and bold designs.
During the height of Corita’s fame, the Catholic Church was reassessing many of its traditions, striving for unity and modernization under Vatican II. And yet not everyone agreed. In 1967, the Los Angeles archdiocese and Archbishop James McIntyre claimed the Immaculate Heart Community’s (IHC’s) approach to education was “communist” and referred to Corita’s work as being “blasphemous.” When the IHC sisters were ordered to end the liberating “renewal innovations” they had come to enjoy—or be asked to leave their teaching posts—many asked to be released from their vows and left in protest.
Corita’s decision to leave the order came a little sooner. In 1968, exhausted from an intense schedule and censorship from the church, Corita took a sabbatical. At the end of her time away, she left the Order and moved to Boston. There, she continued to receive commissions and to create art such as painting the Boston Gas Company’s tanks and designing the iconic “Love” postage stamp.
Corita Kent continues to be celebrated through exhibitions and publications. This book, Make Meatballs Sing: The Life and Art of Corita Kent, introduces young audiences to her story. / Photo by Kristen Gallerneaux
Angela Davis
Angela Davis is an activist, educator, and scholar who was a member of the Communist Party USA and the Black Panther Party. In 1970, Davis was placed on the FBI’s “Most Wanted” list. Guns registered to her name were used in a fatal attempt to free the Soledad Brothers during a courtroom trial. Davis was not present at the event. She fled police, fearing unfair treatment. After her capture, she spent 18 months in prison until being cleared of charges.
For some people, Davis is a controversial figure who believed in non-peaceful protest. To others, she is an inspiration as an outspoken supporter of women’s and civil rights, prison reform, and socialism. In recent years, she came out as lesbian and advocates for LGBTQ+ rights as well as those of Palestinian people.
The following artifacts relate to the impact of Angela Davis’s activism, past and present..jpg?sfvrsn=cc0a3601_2)
Vermont S. Galloway—a WWII veteran—made this “FBI Captures Angela” screenprint at Westside Press to advocate for Davis’s freedom. Galloway was fatally shot by the Los Angeles Police Department in 1972. / THF277084
A parade flier documents the international “Free Angela” movement. The reverse side shows the planned route through Oakland, California. / THF627614
“13 Questions…” was the first interview with Davis while she was incarcerated. Her discussion with Joe Walker covers topics such as the surveillance of Black people, legal corruption, solidarity, and dismal prison conditions. / THF627594
An illustration by Akinsanya Cambon advertises the Black Panther Party’s newspaper and the “Free Breakfast for Children Program,” using Davis’s name. / THF627598.jpg?sfvrsn=c40a3601_2)
Davis appears in a poster by Tongva artist Mer Young for the Amplifier Foundation. This poster shows the continued impact of Davis’s legacy and was created to encourage Black and Indigenous voting in the 2020 election. / THF626361
Listening to Our Community
In 2021, The Henry Ford began to seek community feedback for ways to update and improve our permanent exhibit With Liberty and Justice for All. This work is continuing in 2022.
Stories of movements, social innovators, and political history are difficult to fully capture in museum labels. There is always too much to tell in 100 words or less. To address this, throughout the display of this exhibit, we will be inviting several community partners to contribute their own labels, in their own voices, to foreground the issues they believe matter the most.
By the Curatorial Staff of The Henry Ford. Quiet & Loud Protest is on view in Henry Ford Museum of American Innovation until March 31, 2022.
Civil Rights, art, making, women's history, African American history, Henry Ford Museum, printing
The Deleted Slavery Passage from the Declaration of Independence
 Engraved copy of the Declaration of Independence, one of only 200 copies commissioned by then-Secretary of State John Quincy Adams, printed 1823. / THF149572
Engraved copy of the Declaration of Independence, one of only 200 copies commissioned by then-Secretary of State John Quincy Adams, printed 1823. / THF149572
The Declaration of Independence, formally adopted on July 4, 1776, by members of the Second Continental Congress, was America’s manifesto against British tyranny. Thomas Jefferson, a Virginia delegate to the Continental Congress (and eventually a U.S. president), had been charged with composing the draft of this document.
Most people are familiar with these iconic lines from the Declaration of Independence:
…We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal, that they are endowed by their Creator with certain unalienable Rights, that among these are Life, Liberty and the pursuit of Happiness…
This is the statement that is most memorable. It is the passage that has been invoked repeatedly throughout our history as a call to action, the passage that is still referenced today as the rationale for upholding people’s individual rights.
But there is much more to the Declaration of Independence than these lines. Further down, within a lengthier portion of the document, Jefferson’s initial draft included a scathing denouncement of slavery. If this passage had been retained, our country’s history might have been very different. But it was deleted.
Why did Jefferson—a slaveholder himself—write this passage denouncing slavery, why was it deleted, and what was the long-term impact of that decision?
The Slavery Passage

Print of Thomas Jefferson, 1929, based upon original 1805 portrait by Gilbert Stuart. / THF2295
The memorable first portion of the Declaration of Independence is full of soaring rhetoric derived from the Enlightenment ideals that Jefferson favored. The Enlightenment, an 18th-century European intellectual movement, stressed liberty and equality as natural human rights. The words in this first portion of the document were more philosophical and aspirational than the reality—and, indeed, they have lent themselves to reinterpretation and redefinition throughout our country’s history.
The later portion pertained to specific issues of the time. It contained a list of perceived wrongdoings against the colonists for which Jefferson blamed Great Britain’s King George III. These included the king’s repeatedly interfering with the colonists’ laws and ability to govern themselves; his placement of hostile troops in their midst; and his generally acting like a “tyrant” while violating Americans’ rights (for more on colonists’ mounting frustrations, see our post about the Boston Massacre). Nearly 30 charges were railed at King George III in Jefferson’s first draft, all intended to justify the colonists rebelling against him.
Included in this list was a 168-word passage condemning slavery as one of the many evils foisted upon the colonists by the British crown. Jefferson’s inclusion of this “evil” within this context was a tactically shrewd decision. It was easy to blame King George III for the institution of chattel slavery (that is, the buying and selling of people as property) with the rest of the “long train of abuses.” This was a key point of contention between Great Britain and the colonies.
The first part of the so-called “slavery passage” was aimed directly at the King:
He has waged cruel war against human nature itself, violating its most sacred rights of life and liberty in the persons of a distant people who never offended him, captivating & carrying them into slavery in another hemisphere or to incur miserable death in their transportation thither…
The second part of this passage alluded to a 1775 proclamation by British Lord Dunmore, which offered freedom to any enslaved person in the American colonies who volunteered to serve in the British army to fight against the American patriots:
…he is now exciting those very people to rise in arms among us, and to purchase that liberty of which he has deprived them, by murdering the people on whom he has obtruded them: thus paying off former crimes committed again the Liberties of one people, with crimes which he urges them to commit against the lives of another.
Lord Dunmore’s 1775 proclamation indeed inspired thousands of enslaved African Americans to seek liberty behind British lines. It also incensed American patriots. Including a direct reference to this, Jefferson knew, would further rally colonists behind the cause for independence and their commitment to rebellion.
Deleting the Passage

Engraving of members of the “Declaration Committee” reviewing Jefferson’s draft, Currier & Ives, 1876. In addition to Jefferson, this committee consisted of Benjamin Franklin, John Adams, Roger Sherman, and Robert Livingston. / THF97316
After four members of a small sub-committee reviewed Jefferson’s draft, the entire 56-member Second Continental Congress then debated its merits. The exact circumstances of this debate may never be known, as there is no written record of it. We do know, however, that during this debate, the slavery passage was removed.
Why did this occur?
The short answer is that too many delegates, and the colonies they represented, had a vested interest in perpetuating the institution of chattel slavery. Southern plantation owners insisted that they needed free labor to produce tobacco, cotton, and other cash crops for export. Northern shipping merchants depended upon the trans-Atlantic triangular trade of rum, sugar (generally in the form of molasses), and enslaved Africans. At the time, slavery existed in all 13 colonies, and at least one-third of the delegates to the Second Continental Congress (who would go on to become the signers of the Declaration of Independence) owned slaves themselves.
In addition to their own self-interest, the delegates had a larger intent in mind when they deleted the references to slavery in the document. They realized that this manifesto would inevitably lead to war. This document had to convince thousands of colonists to voluntarily risk their lives in a rebellion against the British. The grievances against King George III needed to be ironclad and compelling. They had to unify Americans from 13 very different colonies and from all walks of life. They needed to clearly distinguish friends from enemies. Removing the slavery passage, the delegates felt, helped clarify their arguments and achieve these goals.
This Connecticut patriot enlisted in the Continental Army just before the Declaration of Independence was formally approved. / THF126080
Finally, there was also a prevailing belief at the time that slavery in America was on the wane—that the general emancipation of slaves was imminent and inevitable. Taking the path of least resistance, the delegates chose not to face this divisive issue head-on. Their delay tactic would not last for long, however, as the issue immediately emerged again during the drafting of the U.S. Constitution in 1787.
Copy of the U.S. Constitution, a rare survivor from 1800, including the text of the founding documents as well as the constitutions of the 15 then-existing states and the Northwest Ordinance, which regulated the Northwest Territory. / THF155864
In the end, the delegates replaced the deleted slavery clause with a passage that instead highlighted King George III’s incitement of “domestic insurrectionists among us”—a direct reference to the British stirring up, encouraging, and supporting warfare between colonists and Indigenous tribes:
He has excited domestic insurrections amongst us, and has endeavored to bring on the inhabitants of our frontiers, the merciless Indian Savages, whose known rule of warfare, is an undistinguished destruction of all ages, sexes and conditions.
This was a statement, the delegates believed, that the colonists could truly rally behind. They made no more changes after that.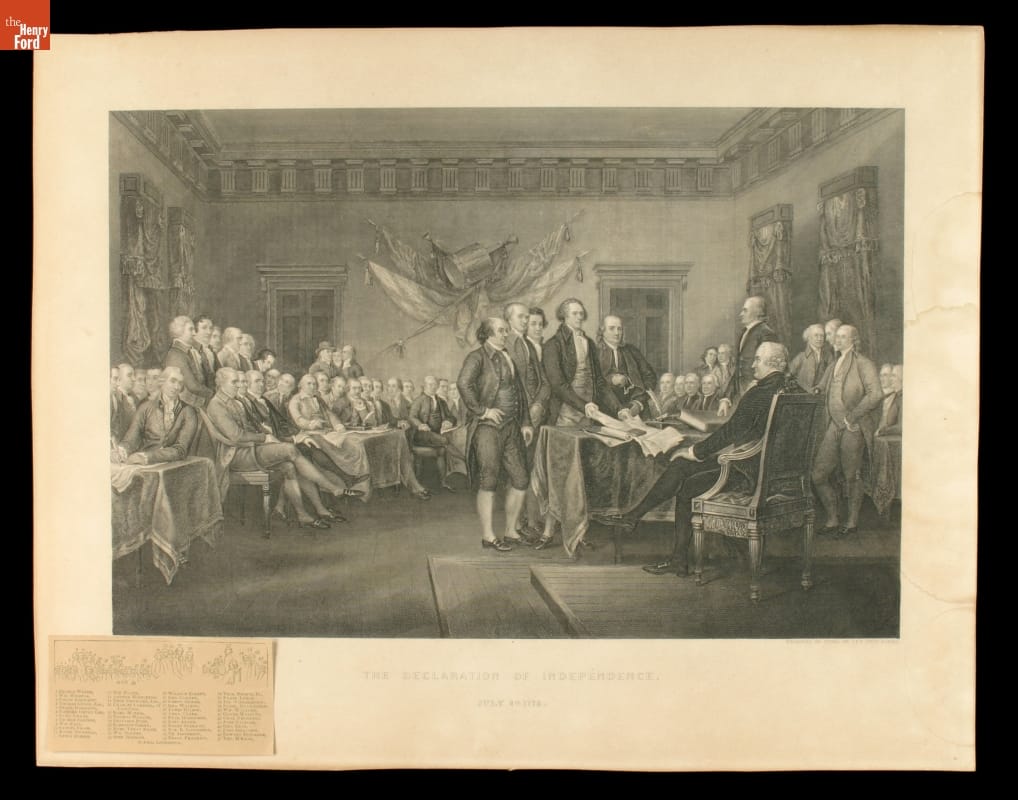
This engraving depicts the June 28, 1776, presentation of the draft of the Declaration of Independence from the five-member Declaration Committee to the entire Second Continental Congress. Engraving made about 1850 by J.F.E. Prud’homme, based upon an 1817 John Trumbull painting. / THF97322
And so, on the fourth day of July, 1776, with the adopted Declaration of Independence in hand, the thirteen American colonies formally declared their independence from Great Britain.
Thomas Jefferson quietly seethed about the changes to his draft of the document, especially the deletion of the slavery passage. He was, in fact, deeply conflicted about the institution of chattel slavery. He understood that his own livelihood depended upon its perpetuation and, over his lifetime, enslaved over 600 people (including his own children by enslaved woman Sally Hemings). At the same time, he bemoaned the existence of slavery and was continually frustrated that he could not extricate himself from its “deplorable entanglement.” As U.S. president in 1807, he passed significant legislation prohibiting the “importation of slaves to any port or place within the jurisdiction of the United States.” But he also suspected that Black people were inferior and supported the popular notion that newly emancipated slaves should leave the U.S. and resettle in Africa or the West Indies.
Impact of the Revised Passage
What the signers of the Declaration of Independence did not realize at the time was that instead of weakening or dying out completely, slavery would become more widespread, profitable, and entrenched in American society. They did not know that slavery would become the central defining problem that would lead to the bloody U.S. Civil War.
The decision to remove the slavery passage and replace it with a passage about “domestic insurrectionists” (i.e., Indigenous tribes) also left a long shadow over the definition of who was considered part of the new republic and who was not—in essence, defining who was an American and who was an outsider (African Americans, both enslaved and free, as well as Native Americans). It consequently ensured that systemic racism against these groups would become as foundational as the American ideal of “life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness."
The deletion of Thomas Jefferson’s slavery passage in the Declaration of Independence had powerful and far-reaching consequences. Little did the Founding Fathers know that that we would still be feeling those reverberations today.
Donna R. Braden is Senior Curator and Curator of Public Life at The Henry Ford. This blog post is part of a series that sheds new light on stories told within the With Liberty & Justice for All exhibition in Henry Ford Museum of American Innovation.
Henry Ford Museum, presidents, African American history, by Donna R. Braden
Piecing Together Black History: A Case Study
For centuries in America, Black history has been relegated to the margins, with stories of Black lives only recorded by those who had the means or the motivation—or perhaps the hope that future generations would value them. The second-class treatment of Black history, the result of entrenched sociocultural discrimination, is painfully obvious to historical professionals looking to the written record for answers about the past lives of Black Americans.
While a major discrepancy still exists between the quality and quantity of Black historical records when compared to white counterparts, scholarship and re-examination, aided by new technologies, have helped in making new and old information alike more accessible. With barriers to information accessibility lessened to some degree, assembling these pieces of information into individual stories remains the biggest and most puzzling challenge. A prime example of this challenge can be found in the analysis of a document from The Henry Ford’s Digital Collections—an 18th-century apprenticeship contract.
This apprenticeship document was gifted to Henry Ford in 1928 by William Van Rensselaer Abdill of Titusville, New Jersey. Abdill was a well-known collector whom Ford and others called upon to locate certain objects from history. This item was most likely part of a larger document collection that Abdill had amassed. / THF129623
On the surface, this apprenticeship document shows no indications of being related to Black history, but a careful examination proves otherwise. To start, there’s a name, “John Thompson” (or “John Thomson,” as signed at the bottom); there’s an age, “fourteen years, eight months, twenty-seven days”; and there’s a date, September 11, 1794. Other information from the document tells us that John Thomson was from Salem, Massachusetts, and was apprenticing to be a “mariner.” A careful sifting of this information through genealogical resources reveals that in May of 1809, this same John Thomson applied for a Seamen’s Protection Certificate. The application confirmed Thomson’s birth in 1780 in Salem, Massachusetts, and described him as a “negro, born-free.”
John Thomson’s application for a Seamen’s Protection Certificate included identifying information. The document states he was about five feet, three inches, in height and had several scars above his left eyebrow, as well as a scar from a smallpox inoculation on his left elbow and marks from a dog bite on his left arm. / Citation: The National Archives and Records Administration; Washington, D.C.; Proofs of Citizenship Used to Apply for Seamen's Certificates for the Port of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, 1792-1871
Further historical context helps illuminate John Thomson’s life and experiences. During the “Age of Sail,” when global commerce was facilitated by sailing ships, the city of Salem, Massachusetts, was a bustling international port. In the centuries before Thomson’s apprenticeship, slavery played a major role in Salem’s maritime economy, not only in the city’s involvement in the slave trade, but in the lives of those who worked its ships and docks. Even after Massachusetts became the first state to abolish slavery in 1783, slavery’s discriminatory legacy continued. As one of the few occupations open to them, free Blacks found life on the sea as a sailor to be a more integrated and less racially tense working environment. In port cities like Salem, these kinds of employment opportunities helped lay the foundation for Black communities in the early years of America.
John Thomson’s 1794 contract also reveals clues about how the then-14-year-old spent the next six years of his work life apprenticed to Captain Robert Emery on the ship Diana. Information on the ship and its captain (in contrast to Thomson) is plentiful. We know that the Diana was built in 1790 up the coast in Amesbury, Massachusetts, and was used to carry trade with Europe. Sometime in 1793, a change of ship masters occurred in New York City and the Diana was transferred to Emery, who was merely 20 years of age at the time.
Information from the first part of the document tells us that Robert Emery was the master of the ship Diana (whose owners were based in Boston), and that John Thomson’s apprenticeship would last just over six years. / THF129623, detail
In 1794, Emery was hiring a crew for an upcoming trip to Bristol, England, and needed an apprentice. Apprenticeships were standard in a variety of trades during this period of American history. Usually, a boy of about 13 or 14 would be indentured to a master until he reached the age of 20 or 21. In return, the master would provide food, clothing, shelter, and, most importantly, training. For Black adolescents like John Thomson, whose opportunities were limited, a stable source of food, clothing, and training could be life changing. Racially integrated crews were common for ships sailing out of Northern port cities. In 1805, five years after Thomson’s apprenticeship ended, Emery hired another racially integrated crew to sail out of Salem for India aboard the vessel Golden Age. Among the group were two local Black men: a “first mate” (next rank under captain) and a “boy” (another name for an apprentice).
As part of the agreement, John Thomson would be provided “meat, drink, apparel, washing and lodging” during his apprenticeship. / THF129623, detail
Threats abounded for Black sailors when John Thomson agreed to his apprenticeship contract in 1794. A year earlier, the 1793 Fugitive Slave Act was passed, giving slaveholders the right to recover an escaped slave. Abuse of the law began immediately, as it offered no procedural protections for free Blacks to avoid being seized as slaves—no right to a lawyer or a trial by jury, or even to speak on their own behalf. Furthermore, the British were struggling to staff a massive navy and actively forced thousands of unwilling American sailors into service. In an effort to stop illegal impressment by the British, Congress began issuing Seamen’s Protection Certificates in 1796, which worked as identification papers and proof of a sailor’s American citizenship. These kinds of papers would have been doubly important to Black sailors who were also under constant threat of being enslaved.
“J.W. Keese” of the “City of New York” notarized the agreement at some point in time. / THF129623, detail
In the years preceding Seaman’s Protection Certificates, around the mid-1780s sailors began carrying papers that helped prove their identity. These could have been copies of parish or town records or a notarized statement by a reputable person who could attest to the bearer’s American citizenship. Notarizing this apprenticeship document, most likely Thomson’s only proof of identification, would have been vitally important. The writings along the side of the document speak to this, as they show that this document was notarized by John Keese of New York City—a notary public, attorney, and founding member of the New York Manumission Society. As New York was a major port city, it’s likely Thomson would have been there at some point, and while the Manumission Society played a paternalistic guardian role in lives of New York’s slaves and free Blacks, it would have been one of the only groups advocating for Black rights in general. For free Blacks like John Thomson, having Keese’s name on the document carried weight if anyone questioned his identity.
The reverse side of the agreement confirms Thomson finished his apprenticeship in Salem on October 8, 1800. / THF129624
We know little about Thomson’s time on the Diana, except for the fact that at some point in the late 1790s, Emery armed the ship for protection against the French. According to the reverse of the contract, Thomson’s apprenticeship ended in Salem in 1800. Details about the remainder of Thomson’s life and career remain lost (or at least very well hidden) to history—whether or not he had a family (some sources suggest he married Violet Wilkins in 1817), if he joined fellow Black sailors in defending the nation during the War of 1812, or even when he died. What has endured though, are the pieces of information that provide enough clues to tell a meaningful part of Thomson’s story—and offer an important lens into the lives of early Black Americans.
Ryan Jelso is Associate Curator, Digital Content, at The Henry Ford. He would like to point out that numerous digital resources were used in the researching of this blog—from genealogical resources like Ancestry.com and academic resources like JSTOR, to the digitized collections of many other institutions.

“The Night Before Christmas” program at Holiday Nights in Greenfield Village. / Photograph by Amy Nasir.
Guests of Henry Ford Museum of American Innovation and Greenfield Village have been captivated by our various dramatic programs for decades at The Henry Ford. And Anthony Lucas’ performances as an historical actor have been essential in bringing our stories to life throughout many time periods and historical contexts. I had the honor of sitting down with Anthony, 2010 winner of The Henry Ford’s Steven Hamp Award, to chat about his 20 years of theatrical work at The Henry Ford.
You’ve been performing at The Henry Ford since the fall of 2000. What was your first project here?
I started as a replacement actor when another actor was out sick, and I performed in a program called “Gullah Tales” near the Hermitage Slave Quarters. After this, they called me back to do more performances.
How did you get into acting and what inspired you to act?
My interest to become an actor goes back to when I was five years old, believe it or not. I used to watch a gentleman named Bill Kennedy, a local TV host in Detroit who would show a lot of black-and-white Hollywood movies on Sunday afternoons. I would watch actors like James Cagney, and I said in my mind: “Wow, I want to do that!” I have a lot of favorite actors, but James Cagney was the first one because of his energy and his versatility. He could play a lot of different roles other than playing the bad guy. All the movies I watched on Bill Kennedy at the Movies were very entertaining, and they made a big impression upon me, including all the musicals and the films that starred Shirley Temple, Humphrey Bogart, Edward G. Robinson, and Bette Davis—the Golden Age of Hollywood.
What were your first theatrical roles and when did you perform them?
I really didn't get the opportunity to act until at the end of the 11th grade in high school. The following year, I did two plays. One was kind of a historical play dealing with Black history. It was called “In White America,” and it was a series of vignettes and monologues about civil rights and the Black struggle for freedom in the United States. And the other play was a kind of comedy farce called “Day of Absence.” The story took place in the South, and it dealt with what would happen if one day all the Black folks had suddenly disappeared. My performances took place in the early 1970s. We were coming right out of the sixties with the civil rights movement and the Black power movement. And so that was my start. I went on to study theater at Western Michigan University and performed in various shows with Detroit Repertory Theatre and Plowshares Theatre Company.
“Elijah: The Real McCoy” program in the museum. / Photograph by Kristina Sikora (KMS Photography)
You’ve performed in several programs at The Henry Ford, which we’ll get into in a moment. But first, which one stands out as your favorite?
I love all the shows that I do, but one of my most favorite programs is “Elijah: The Real McCoy,” which I performed in both the village and museum. Elaine Kaiser, who has since retired [as Manager of Dramatic Programs at The Henry Ford], wrote it brilliantly. She wrote it for me to perform at Discovery Camp. Every show was very rewarding, and I just loved working with the kids during camp and seeing them at shows. The story starts with Elijah McCoy as a young kid, and the scenes travel through his achievements and struggles until he reaches his success as an inventor, and then into his old age. I loved to perform each stage of his life and see the kids’ reactions.
Photograph by Kristina Sikora (KMS Photography)
Have there been any challenges you’ve encountered while performing?
Well, here’s a story that’s kind of funny. One summer in the village, I was very busy. While I was at Town Hall doing a couple of Elijah McCoy shows, I would need to change into a different period costume and get to Susquehanna Plantation to do “North Star Tales” as fast as I could. And then I would hurry up and go back to Town Hall, change, and do another Elijah McCoy. Thankfully, Elaine Kaiser loaned me her bike, so I could ride it between shows. So, it was quite exciting!
“How I Got Over” program at Susquehanna Plantation. / Photograph by Roy Ritchie
I’ve attended your performances at Susquehanna Plantation many times and have always been inspired when participating with other guests as we jumped from the porch steps yelling, “Freedom!” How long have you been performing at Susquehanna, and are there any other similar programs you perform in?
There were a few different shows we did at Susquehanna, and they go back to 2003, right after the renovation of the village. There is “How I Got Over,” “Tally’s Tales,” and a newer version called “North Star Tales,” which were all themed around the stories of slavery and endurance on the plantation. Last year in 2021, I narrated the North Star Gospel Chorale’s performance on the porch of Susquehanna as part of Salute to America: Summer Stroll. That was the first year, and it was really a great experience. We really enjoyed that. It's really a powerful show and I was happy to be a part of that. The Chorale also performed in the museum in February 2020, right before the pandemic, which was livestreamed on Facebook.
“I’ve Seen the Mountain Top” speech at National Day of Courage in the museum. / Screenshot from YouTube
You are also a big part of the “Minds on Freedom” program in the museum. When did that start and how did it develop?
Yes, this program started in 2004, and it was a combination of two shows—a musical act, and then a dialogue part about the Civil Rights Movement. It was merged into one show called “Minds on Freedom,” which was performed in the museum around our Celebrate Black History program in February. There was also our special celebration of the Emancipation Proclamation in June 2011, which I enjoyed being a part of. And during the National Day of Courage, celebrating Rosa Parks’ 100th birthday on February 4, 2013, I performed Martin Luther King, Jr.’s “I’ve Seen the Mountain Top” speech. That's always an honor any time I get a chance to express the words of Dr. King. He was a great man, a great orator, a great minister, and a great leader. And he gave his life for us to believe them. So any time you try to deliver his speeches, you’re never going to be like Dr. King. But I use my own approach and try my best to get the spirit across.
“Elijah: The Real McCoy” program in the museum. / Photographs by Kristina Sikora (KMS Photography)
Many guests are familiar with your performances at our Hallowe’en in Greenfield Village and Holiday Nights in Greenfield Village events. How and when did these roles begin?
Oh, yeah, performing “The Tell-Tale Heart” by Edgar Allen Poe goes way back with me, because it was one of the first dramatic readings I recited in high school. My mother coached me. I think if my mother had pursued acting, she may have been a pretty good actress. She helped me bring the story to life. Around 2003, Elaine Kaiser asked me to dramatize this short story for Hallowe’en from the point of view of a murderer descending into paranoia, haunted by the thumping sound of the murdered man’s heart. The program is different from Holiday Nights, because I have set times for shows. So I usually don't have a chance to interact with the audience in-between shows as much as I would like. Interacting with the audience afterwards whenever possible is a special part of being there. I'm not there just because I'm an actor to do shows. I'm there to be a part of The Henry Ford and to interact with the guests and help create that experience for them. It’s very special, unique, and moving to interact with the guests. So that's how I approach it.
I started performing at Holiday Nights just before I performed at the Hallowe’en event. Initially around 2003, I was working with a few other actors, and we were moving around the village doing a variety of poems and Christmas carols. And it was around 2004, I performed Clement Clarke Moore’s “A Visit from Saint Nick,” which we generally call “The Night Before Christmas.” I performed it as a solo act and was relocated outside of Town Hall and later to a warming fire. It’s developed into a very special event because of how guests react. There was one guy who proposed to his girlfriend at my warming fire. There are so many people with stories of their own, making Holiday Nights and the village a big part of their lives. Holiday Nights is a whole story in itself. I started adding an introduction to the performance rather than just solely dramatizing the poem. I started talking about Christmas in early America. And then I would ask guests about all the different holiday foods and dishes they like, and finally I would ask: Do you like Christmas cookies? I would then ask the big question: Do you have any with you tonight?
After this, guests started bringing me Christmas cookies every year. I come home with all sorts of cookies, sugar cookies, and chocolate chip cookies and all. Oh, yeah, it's funny. But it's great, though, because people come year after year and sometimes they tell me they used to bring their children and now they're all grown up. I'm like, wow, this is a reminder of how long I've been doing it. And it's so rewarding; sometimes I look out and see people that are moved. They get emotional and so it's wonderful. And the children are the best, they can just make you feel like a million bucks. In December 2020, I recited “The Night Before Christmas” for a video during the pandemic. That was a real different take on it because they had me come in and sit down and have a storybook in my hand. So I had to rework it so it could fit that format. And I like that too. It was very comfortable and warm. That was a real nice change of pace.
“The Tell-Tale Heart” program at Hallowe’en in Greenfield Village. / Photograph by Kristina Sikora (KMS Photography)
Do you have any other stories about interacting with guests you’d like to share?
Sure. I was performing Elijah McCoy at the Town Hall one day, and there is a point where I would walk up the steps of the stage. I was playing the elderly Elijah, and I asked for volunteers from the audience to help me up the steps. So, this one little girl came up to me and she said: your tie is crooked. And she starts straightening my tie. Sometimes you just have to roll with it. That was a beautiful moment.
Another time, there was this couple that followed my shows. They took pictures of me performing Elijah McCoy in the village and “Minds on Freedom” in the museum, and other performances. The wife put together a scrapbook of their photos, and it had all these pictures and a beautiful cover. They gave it to me as a gift. I was just so speechless, you know, that they took time to create it over several months, putting this book together. I was very moved by it.
Amy Nasir is Digital Marketing Specialist and former Historical Presenter in Greenfield Village at The Henry Ford.
Michigan, Dearborn, 21st century, 2020s, 2010s, 2000s, The Henry Ford staff, Holiday Nights, Henry Ford Museum, Hallowe'en in Greenfield Village, Greenfield Village buildings, Greenfield Village, events, Civil Rights, by Amy Nasir, African American history, actors and acting, #Behind The Scenes @ The Henry Ford
A Rosa Parks Baseball?: Inspiring Curt Flood's Battle with Major League Baseball
 Baseball autographed for All-Star centerfielder Curt Flood by one of his heroes, civil rights icon Rosa Parks. / THF96558
Baseball autographed for All-Star centerfielder Curt Flood by one of his heroes, civil rights icon Rosa Parks. / THF96558
Curt Flood was an All-Star, Gold-Glove centerfielder for the powerhouse St. Louis Cardinals baseball team of the 1960s. He undoubtedly signed thousands of baseballs during and after his career. So why would Flood save a baseball signed by Rosa Parks among his personal effects?
The ball is part of a story of inspiration, courage, and perseverance.
Inspired to Take a Stand
Curt Flood grew up in Oakland, California, and had no direct experience with the intense racism of the Jim Crow South. He was among the first generation of Black players in Major League Baseball. In 1956, as a 19-year-old minor leaguer in the Deep South, Flood came face-to-face with the virulent racial hatred that had arisen in the wake of the 1955 Supreme Court decision outlawing segregation in schools, and from the ongoing Montgomery, Alabama, bus boycott inspired by Rosa Parks. It was the courage shown by Rosa Parks, Jackie Robinson (the player famous for breaking Major League Baseball's color barrier), and others that gave Flood the strength to persevere through his two-year minor league stint.
Flood joined the Major Leagues when he was signed by the St. Louis Cardinals in 1958. He and two of his new teammates, Bill White and Bob Gibson, became increasingly outspoken about segregationist aspects of the Cardinals operation. These men successfully pressed the organization to patronize integrated hotels and restaurants. Flood also joined Jackie Robinson at NAACP rallies across the South.
Curt Flood was featured on the August 19, 1968, cover of Sports Illustrated. The issue, pictured here with Flood’s St. Louis Cardinals hat, called him "Baseball's Best Centerfielder." / THF76590
Fighting the Reserve Clause
Flood's stellar 12-year career with the Cardinals ended suddenly in 1969, when he was traded to the Philadelphia Phillies. The Phillies were a team going nowhere, with a fan base and management that were hostile to Black players. Flood had little desire to be part of that team. But the reserve clause gave Flood no choice in the matter. This clause was a standard part of every baseball player's contract, requiring him to play wherever the owners wanted him to play. The player had no say in the matter.
Flood's only options were to go along with the trade or retire. His first instinct was to retire. But, after reconsidering, he decided to challenge the reserve clause and sue Major League Baseball. Flood knew that this action would, in effect, end his baseball career and that he personally would gain little in the end. But the reserve clause made Flood feel like a piece of property, and he could not let that injustice stand.
Curt Flood's letter to baseball commissioner Bowie Kuhn was brief and to the point:
Dear Mr. Kuhn:
After twelve years in the Major Leagues, I do not feel that I am a piece of property to be bought and sold irrespective of my wishes. I believe that any system which produces that result violates my basic rights as a citizen and is inconsistent with the laws of the United States and of the several States.
It is my desire to play in 1970, and I am capable of playing. I have received a contract offer from the Philadelphia Club, but I believe I have the right to consider offers from other clubs before making any decisions. I, therefore, request that you make known to all the Major League Clubs my feelings in the matter, and advise them of my availability for the 1970 season.
Sincerely yours, Curt Flood
Lonely Path to the Supreme Court
As expected, Major League Baseball rejected Flood’s request. Over the next two and a half years, Flood, with the support of Marvin Miller of the Players Association (the fledgling professional baseball players' union), pursued his case in court, then in appeals court, and finally to the United States Supreme Court. At the inception of the suit, Flood became one of the most hated men in baseball—he was criticized in the press for trying to destroy baseball and received mountains of hate mail from fans. But it was the lack of support from active players that hurt Flood the most. Some supported Flood privately but feared retribution if they spoke out. Others were outright hostile and tried to undermine the suit even though it would benefit all players. Only baseball outsiders testified on Flood's behalf: his hero, Jackie Robinson; Hank Greenberg, who battled anti-Semitism throughout his career with the Detroit Tigers; and the iconoclastic Bill Veeck, who had owned several major and minor league baseball teams.
Curt Flood (left) and pitcher Bob Gibson had been close friends since their days in the minor leagues. Gibson privately supported Flood in his activism, but despite being one of the best pitchers in the game, he feared he would be ostracized from baseball if he backed Flood publicly. / THF98488
The court battles took a physical and emotional toll on Flood. He fell out of shape physically and turned from a social drinker to an alcoholic. The relentless negative attention from the press and fans forced Flood out of the country, first to Denmark, and later to Spain. He lost touch with his children and, by 1975, was nearly destitute and homeless. Flood was despondent and depressed. In 1978, Richard Reeves interviewed him for Esquire magazine as part of a series on men who had stood up to the system. Reeves said, "He was about the saddest man I ever met."
The closely divided Supreme Court ruled against Flood in the end. The majority opinion said, in effect, that the reserve clause was "an anomaly," but that it was Congress's job to fix it, not the courts’. Despite the Supreme Court loss, Flood's fight had created an opening to challenge baseball's reserve clause on the bargaining table. Within a few years, Jim "Catfish" Hunter became the first free agent, followed closely by Andy Messersmith and Dave McNally. While Curt Flood lost the case, his efforts transformed the relationship between owners and players across professional sports, and for people with unique and valuable skills in the world at large.
Curt Flood signed this copy of the Supreme Court summary report of his suit against Major League Baseball. / THF98457
Recovery and Recognition
After more than a decade in a personal wilderness, Flood began to turn his life around with the help of friends. He was treated for alcoholism in 1980, re-married in 1986, gained a new family, and reconnected with the children of his first marriage. Flood took up the late Jackie Robinson's cause, pushing for more diversity in the management of baseball. Along with other former players, he co-founded a group known as the Baseball Network for that purpose.
In 1987, Curt Flood received the NAACP Jackie Robinson Sports Award. While he was never hired for a position in baseball management, Flood became a regular at old-timers’ games. There, many former players took the opportunity to thank him personally. In 1994, Flood was featured in Ken Burns’ Baseball documentary and attended the premiere, where he met President Bill Clinton and Hillary Clinton. Not long after, he met another hero from his youth, Rosa Parks, who signed a baseball for him. Flood wrote to friends in a Christmas letter that year, "I am in the process of living happily ever after."
In 1987, the NAACP recognized Curt Flood's fight by awarding him the Jackie Robinson Sports Award. / THF76582
In the summer of 1995, Flood developed throat cancer; he died on January 20, 1997. During that year and a half, many people visited him to express gratitude for what he had done for baseball and for society at large. At his death, Curt Flood was eulogized by many, including Jesse Jackson and conservative columnist George Will, who compared him to Rosa Parks.
Curt Flood and his wife, Judy Pace Flood, with Rosa Parks in 1994. / THF98496
While in retrospect, it may seem as though changes in society are predetermined and expected, Curt Flood's experience shows that they are not a sure thing—and they are never easy. The reserve clause was a legal anachronism that stripped players of their freedom to control their own careers. It took a successful man—inspired by heroes who had taken similar steps before him—who was willing to give up everything to make that change occur.
Jim McCabe is former Curator and Collections Manager at The Henry Ford. This post originally ran in February 2010 as part of our “Pic of the Month” series. It was updated for the blog by Saige Jedele, Associate Curator, Digital Content, at The Henry Ford.
1970s, 1960s, Pennsylvania, 20th century, Missouri, sports, Rosa Parks, by Saige Jedele, by Jim McCabe, baseball, African American history

